Figure 3.
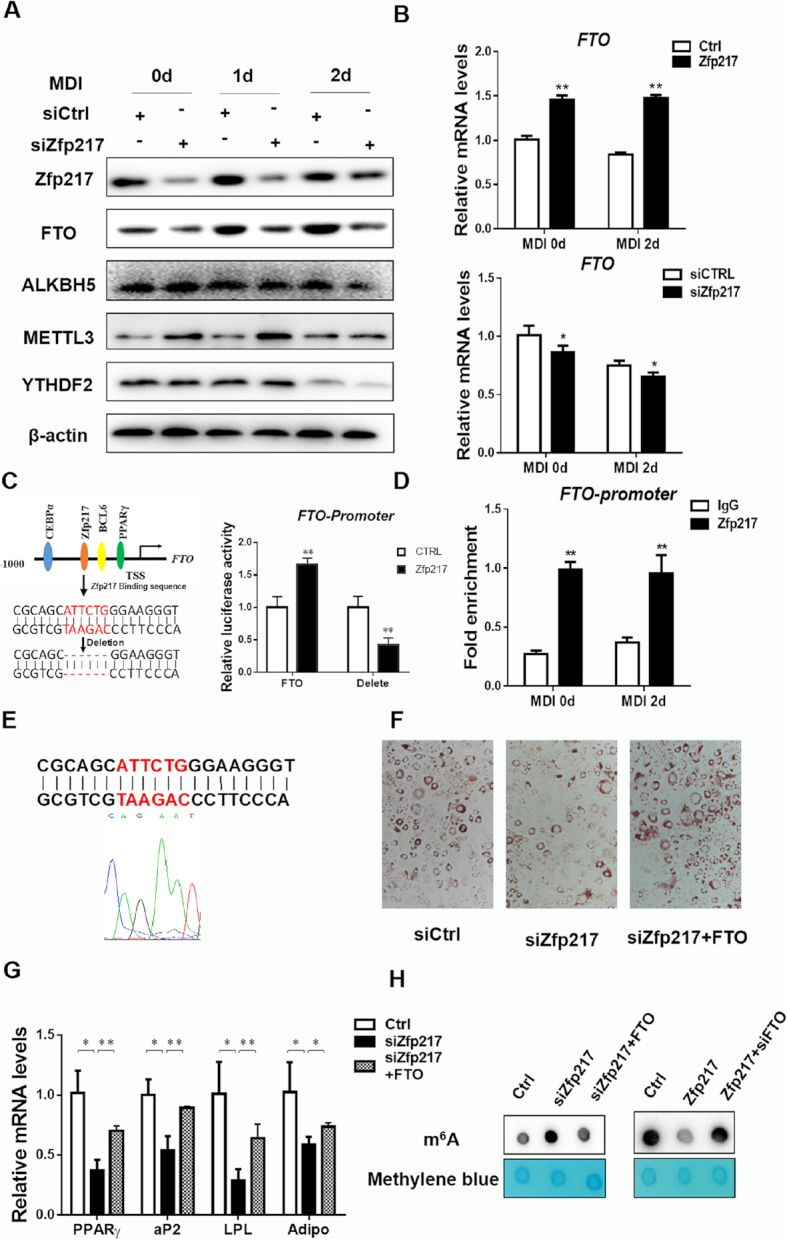
Activation of FTO transcription by Zfp217 for adipogenesis. (A) Protein expression levels of m6A-related proteins during MDI treatment in Zfp217 knockdown cells were detected by western blot (n = 3). β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) mRNA levels of FTO in 3T3L1 cells with overexpression and knockdown of Zfp217 were detected by QPCR (n = 3). (C) Left panel: schematic representation of transcription factor binding promoter of FTO; right panel: dual-luciferase activity of normal and binding site-deleted FTO promoter by overexpressing Zfp217 in HEK293T cells (n = 3). (D) ChIP-QPCR assay was used to measure the binding of Zfp217 on FTO promoter in 3T3L1 cells with or without treatment of MDI (n = 3). Total chromatin was indicated as input and IgG was used as a negative control. (E) The position of the amplified regions of Zfp217 binding sequence in FTO promoter was indicated. (F) The effect of Zfp217 knockdown or together with overexpression of FTO on adipogenesis of 3T3L1 cells (n = 3). (G) mRNA expression levels of adipogenic genes were measured in 3T3L1 cells with Zfp217 knockdown or together with overexpression of FTO and treated with MDI for 6 days (n = 3). (H) The effect of overexpression (or knockdown) of Zfp217 or together with depletion (or overexpression) of FTO in 3T3L1 cells on m6A modification (n = 3). Presented as means ± SD (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).
