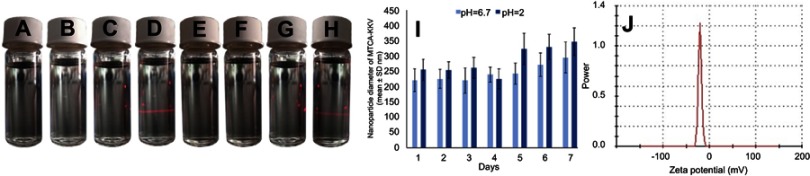
Figure 3.
Tyndall effect, particle size and zeta potential of MTCA-KKV in ultrapure water. (A) Feature of ultrapure water of pH 6.7; (B) Feature of 0.1 μM solution of MTCA-KKV in ultrapure water of pH 6.7; (C) Feature of ultrapure water of pH 6.7 with the radiation of 650 nm laser; (D) Feature of 0.1 μM solution of MTCA-KKV in ultrapure water of pH 6.7 with the radiation of 650 nm laser; (E) Feature of ultrapure water of pH 2.0; (F) Feature of 0.1 μM solution of MTCA-KKV in ultrapure water of pH 2.0; (G) Feature of ultrapure water of pH 2.0 with the radiation of 650 nm laser; (H) Feature of 0.1 μM solution of MTCA-KKV in ultrapure water of pH 2.0 with the radiation of 650 nm laser; (I) Seven-days’ size of MTCA-KKV in pH 6.7 and pH 2.0 ultrapure water (0.1 μM); (J) Zeta potential of MTCA-KKV in pH 6.7 ultrapure water (0.1 μM).
Abbreviations: MTCA-KKV, (1R,3S)-1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxyl-Lys(Pro-Ala-Lys)-Arg-Gly-Asp-Val.