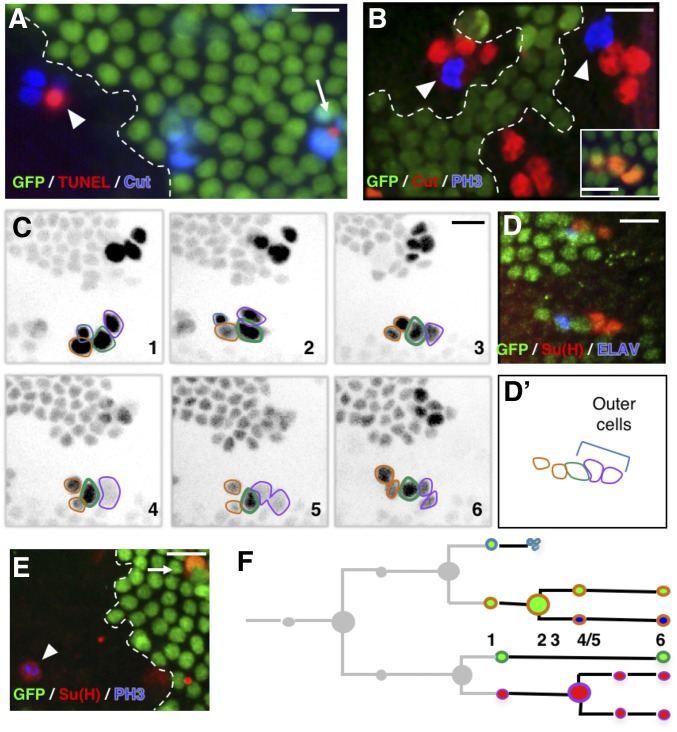
Figure 2.
Extra mitoses in Ttk69-mutant socket cells. (A, B, and E) Ttk69 clones, outlined by a white line, are detected by the absence of GFP (green) in fixed tissues. (A) Apoptosis occurred at the same time in mutant (arrowhead) and control (arrow) SOs. Sensory cells (blue); apoptotic cells (TUNEL staining, red). (B) Extra mitoses [PH3 immunoreactivity (blue), arrowheads] in a Ttk69-mutant SO composed of four cells (red); control cluster in the inset. (C and D) Correlative four-dimensional live imaging and lineage analysis showing an extra division of socket cells. A Ttk69 clone was identified by a lack of GFP expression in epithelial cells and SOs inside the clones were imaged. (C) Representative frames (1–6), depicted in inverted fluorescence, from a time-lapse recording of one Ttk69-mutant SO at 19-hr APF. Glial cell outlined in blue, pIIb and its progeny in orange, the shaft cell in green, and the socket cell and its daughter in purple. Frames 4 and 5, division of the socket cell. Apoptosis of the glial cell between frames 2 and 3. (D and D’) Immunostaining and schematic representation of the same cluster after the time-lapse recording shown in (C). Nonclonal epithelial and sensory cell (GFP expression, green), neuron (ELAV, blue), and socket cell [Su(H), red] immunoreactivity. (E) Cell divisions in full-determined socket cells. PH3 (blue) and Su(H) (red) immunoreactivity was detected in the same cell (arrowhead); control socket cell (arrow). (F) Schematic view of the lineage shown in (C). Cells are encircled using the same color code as in (C) and filled with the same color as in (D). Bar, 10 μm. APF, after pupal formation; SO, sensory organ; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling.