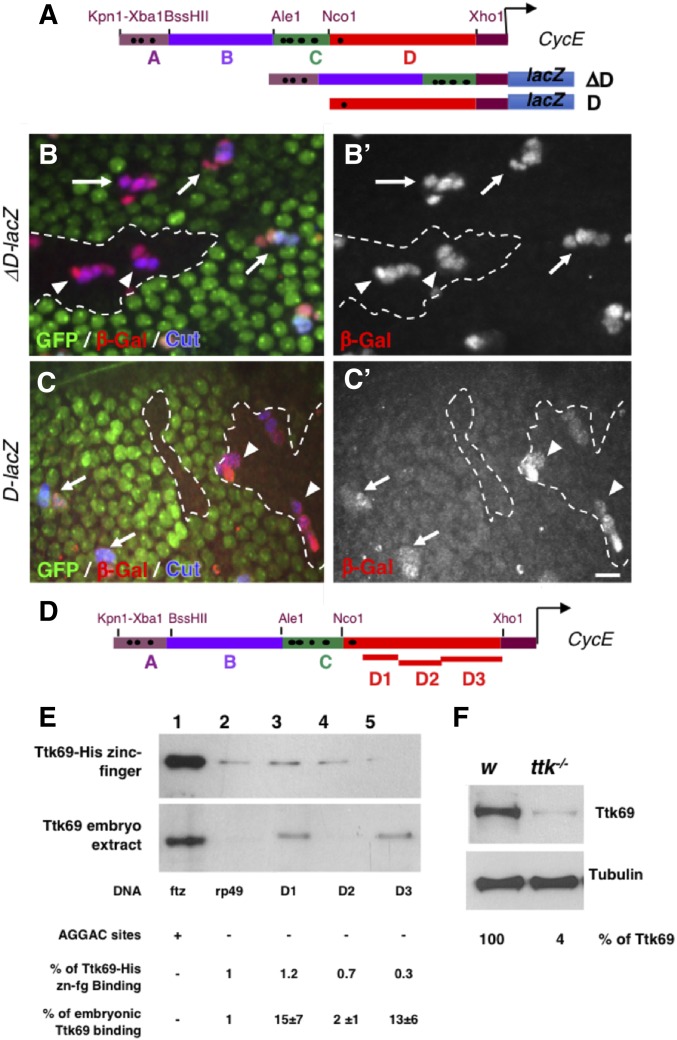
Figure 5.
Ttk69 binds indirectly to the CycE promoter. (A) Diagram of CycE promoter depicting the four specific regions analyzed (A–D). Black dots, canonical AGGAC Ttk-binding sites. ΔD and D CycE transcriptional reporters bearing a deletion of the D region and only the D region, respectively. (B and C) Expression pattern of ΔD-lacZ (B and B’) and D-lacZ (C and C’) in control (arrows) and Ttk69-mutant SOs (arrowheads). Ttk69 clones outlined by a white line were detected by the absence of GFP (green). Sensory cells (Cut immunoreactivity, blue) and expression of CycE transcriptional reporters (β-Gal immunoreactivity, red and bottom panels). (D) As in (A), showing the regions of the D fragment analyzed (D1–D3). (E) DNA-mediated pull-down assay using Ttk69-his-zinc finger (top) and whole Ttk69 protein from an embryo protein extract (bottom). Magnetic beads were coated with: lanes 1 and 2, as in Figure 4B; and lanes 3, 4, and 5 with the D1, D2, and D3 regions, respectively, of the CycE promoter. (F) Detection of Ttk69 protein from a protein extract of one control (white) and one Ttk69-mutant embryo. Tubulin, loading control. Bar, 10 μm for (B and C). β-Gal, β-galactosidase; SO, sensory organ.