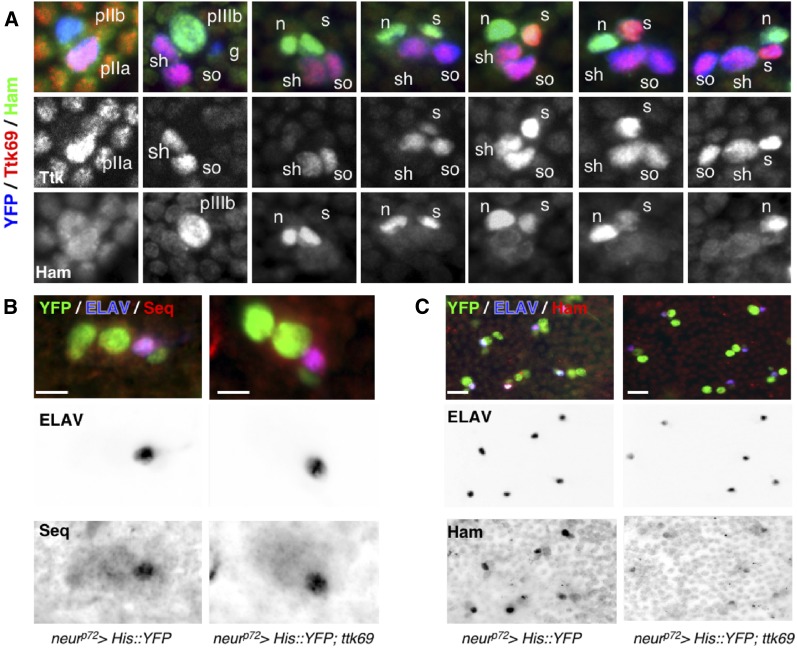
Figure 6.
Ttk69 downregulates hamlet but not sequoia expression. (A) Complementary expression pattern of Ttk69 and Ham proteins in bristle sensory cells. Ttk69 and Ham expression in bristle sensory cells at progressive stages of development from 18–28-hr APF. Sensory cells are shown in blue (YFP staining), Ttk69-positive cells in red (shown as a separate channel in the middle panels), and Ham-positive cells in green (shown as a separate channel in the bottom panels). The sensory cells shown are the precursor cells pIIb, pIIa, and pIIIb, and the terminal cells: glial cells (g), sheath cells (s), neurons (n), shaft cells (sh), and socket cells (so). Ttk69 is first detected in pIIa cells and their daughter cells, and later in the sheath cells. Ham is first detected in pIIIb cells and their daughter cells, before disappearing from the sheath cell when Ttk69 appears in this cell. (B and C) Ttk69 overexpression represses hamlet but not sequoia expression. Analysis of Sequoia (Seq) (B) and Ham (C) protein accumulation after specific expression of Ttk69 in sensory cells. Sensory cells (green); neurons (blue), Ham and Seq (red). ELAV (middle panels), Ham, and Seq channels (right panels) are shown in inverted color. Bar, 5 μm in (A and B), 10 μm in (C). APF, after pupal formation; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.