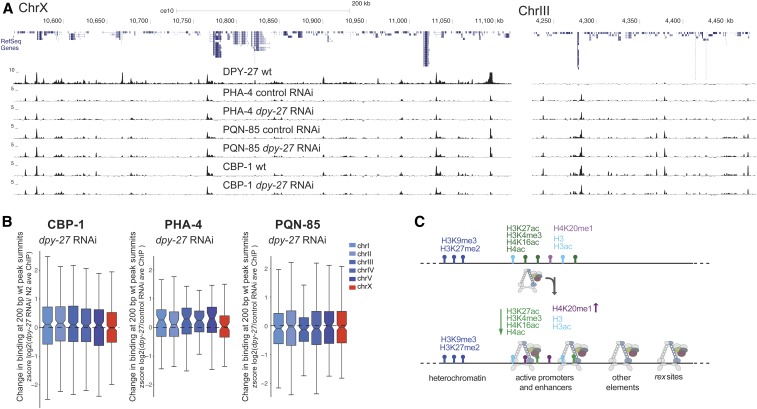
Figure 6.
DCC knockdown does not indiscriminately reduce protein binding as measured by ChIP-seq. (A) ChIP-seq profiles of DPY-27 (condensin IDC subunit), PHA-4 (FOXA transcription factor), PQN-85 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae Scc2p homolog), and CBP-1 (putative H3K27 acetyltransferase) in representative regions on chromosomes X and III. (B) Analysis as in Figure 3I, plotting changes in protein binding across 200-bp wt peak summits. CBP-1, PQN-85, and PHA-4 levels on the X chromosomes did not change significantly upon DCC knockdown. (C) Summary of DCC binding and regulation of histone modifications on the X chromosomes. DCC-binding sites coincide with gene regulatory elements marked by accessible chromatin on the X. The majority of these elements also contain histone modifications associated with active transcription. The remaining include recruitment elements and sites that do not contain the analyzed histone modifications. DCC activity correlates with X-specific changes in the level of specific histone modifications (denoted by up and down arrows). ave, average; ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; Chr, chromosome; DCC, dosage compensation complex; RNAi, RNA interference; wt, wild-type.