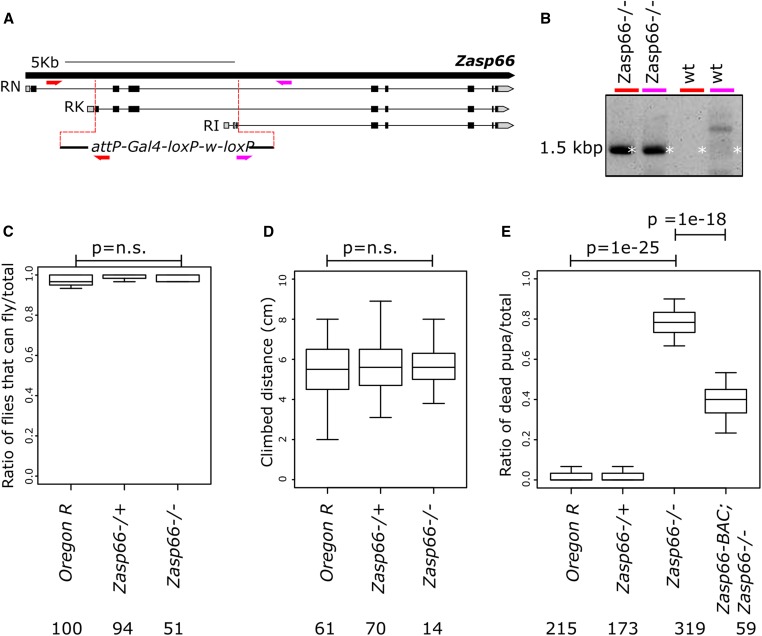
Figure 5.
The Zasp66 null mutant flies show high pupal lethality. (A) Cartoon of Zasp66 genomic locus with selected transcripts. The gRNA-targeted break points are shown as red dotted lines. The replacement cassette is shown at the bottom. Primer pairs used for validation of the mutant are shown in different colors. (B) Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of PCR products obtained from Zasp66 homozygous mutant flies and wild-type (wt) flies. The colored lines at the top of the gel correspond to the primer pairs drawn in (A). (C) Boxplots of the ratio of flies able to fly in different genetic backgrounds. (D) Boxplots of the climbing distance in flies with different genetic backgrounds. (E) Boxplots of the ratio of dead pupae in different genetic backgrounds. The P-values were adjusted by Bonferroni correction and are shown for selected genotype pairs. Number of flies tested is given for each genotype.