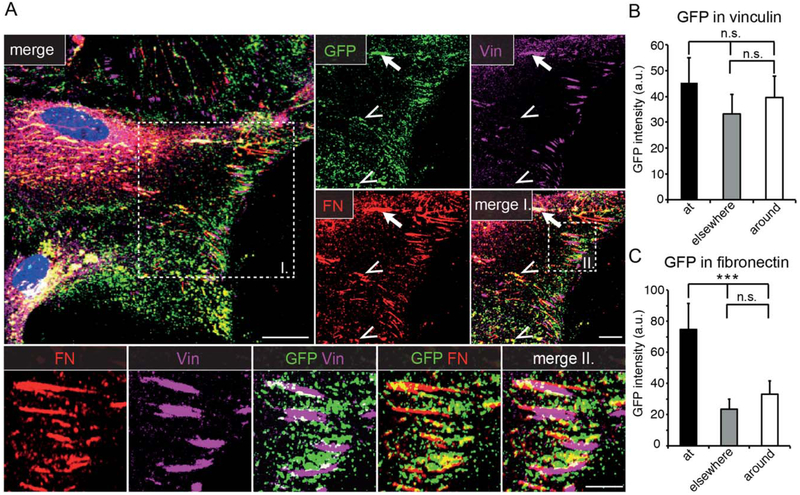
FIGURE 2:
VEGF-GFP is directed to cell-matrix adhesions. A: Confocal images of VEGF-GFP transduced, polarized astrocytes stained for markers of focal (vinculin, Vin) and fibrillar adhesions (fibronectin, FN) show that VEGF accumulates mainly in the vicinity of fibrillar adhesions and colocalizes with FN (insert I, arrowheads) or both with FN and Vin (insert I, arrow). Bars: 20 μm (main), 10 μm (insert I), and 5 μm (insert II). B: Comparison of average GFP intensity “at” Vin+ regions, 3 μm “around” or “elsewhere” in the cells, suggests a tendency for association to focal adhesions. a.u., arbitrary units, mean ± SEM, 70 cells from 3 experiments, repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test, n.s.: nonsignificant difference. C: Average GFP intensity is significantly higher “at” FN+ regions than 3 μm “around” or “elsewhere,” indicating that VEGF associates preferentially to fibrillar adhesions. Mean ± SEM, 70 cells from 3 experiments, repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test *** P<0.001; a.u., arbitrary units