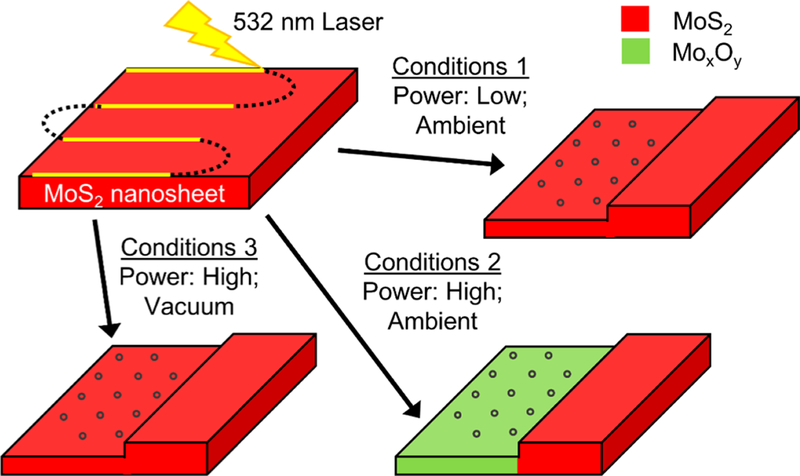
Figure 8.
Laser-induced thinning conditions mostly result in nanoparticle formation (blue circles) on a MoS2 surface; however, different conditions impact surface chemistry. (1) Low-power laser and the presence of atmospheric oxygen retains the MoS2 chemical structure. (2) High-power laser and the presence of atmospheric oxygen results in molybdenum oxidation. (3) High-power laser in the presence of vacuum also retains MoS2 chemical structure.