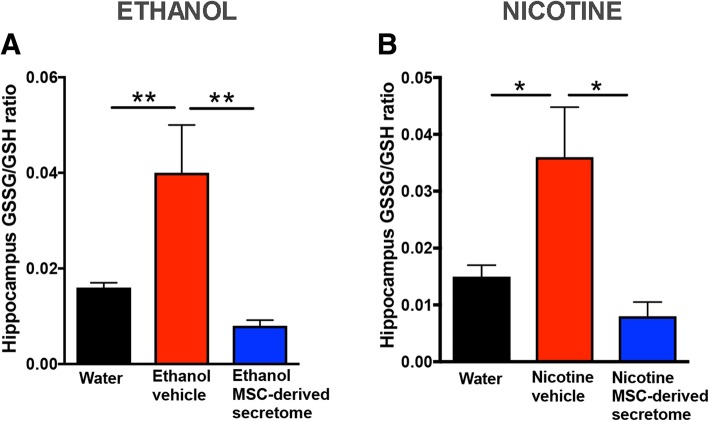
Fig. 4.
Intranasal administration of adipose tissue-derived MSC secretome reduced hippocampus oxidative stress (assessed by GSSG/GSH ratio) induced by chronic ethanol and chronic nicotine intake. The hippocampi were obtained from rats chronically drinking ethanol or nicotine immediately after 60 min of re-exposure to ethanol or nicotine solution, following a 2-week deprivation of ethanol or nicotine. a Chronic ethanol drinking rats treated with vehicle displayed an increased GSSG/GSH ratio (red bar) versus ethanol-naïve rats drinking only water (black bar). Administration of five intranasal doses of MSC secretome, administered at weekly intervals to chronic ethanol drinking rats, normalized the GSSG/GSH ratio (blue bar) (one-way ANOVA: F2,12 = 11.0, p < 0.001; Bonferroni post-hoc: p < 0.01, water drinking versus ethanol-vehicle; p < 0.01, ethanol-secretome versus ethanol-vehicle; n = 5 per group). b Chronic nicotine-drinking rats treated with vehicle displayed an increased GSSG/GSH ratio (red bar) versus naïve rats drinking only water (black bar). Administration of five intranasal doses of secretome, administered at weekly intervals to chronic nicotine drinking rats, resulted in the normalization of the GSSG/GSH ratio (blue bar) (one-way ANOVA: F2,9 = 7.26, p < 0.01; Bonferroni post-hoc analysis: P < 0.02, water drinking control rats versus nicotine-vehicle; p < 0.01, nicotine-secretome versus nicotine-vehicle; n = 5 per group)