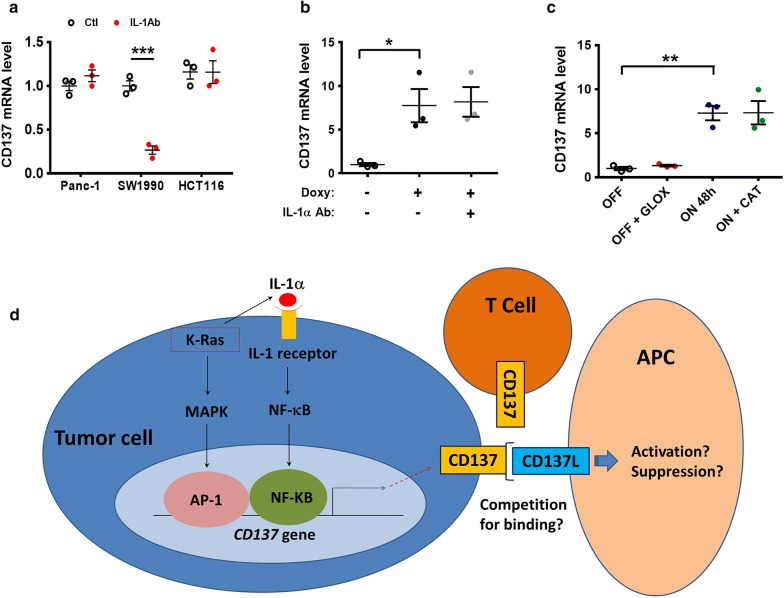
Fig. 5.
Induction of CD137 expression by K-Ras through MAPK and NF-kB pathways. a The indicated three cancer cell lines were incubated with 1 μg/mL neutralizing anti-IL-1α antibody for 48 h. CD137 mRNA was measured by real-time PCR. b T-Rex/K-Ras cells were incubated with 100 ng/mL doxycycline and 1 μg/mL neutralizing anti-IL-1α antibody for 48 h. CD137 mRNA was measured by real-time PCR. c T-Rex/K-Ras/off cells were incubated with 20 ng/mL glucose oxidase for 48 h. T-Rex/K-Ras/on cells were incubated with 50 μg/mL catalase for 48 h. CD137 mRNA was measured by real-time PCR. d Schematic model depicting the likely molecular mechanisms by which K-Ras regulates CD137 gene transcription. Oncogenic K-Ras signal activates two parallel pathways through MAPK and NF-κB signaling. K-Ras enhances the secretion of IL-1α, which in turn stimulates NF-κB signaling to enhance CD137 expression. Data in a–c are presented as mean ± SEM of three repeated experiments. Statistical analysis: Two-tailed unpaired t-test for a–c. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. AP-1 activator protein 1, APC antigen-presenting cells, CAT catalase, CD137 tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9, CD137L tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9, GLOX glucose oxidase, IL-1α interleukin-1 alpha, IL-1Ab neutralizing anti-IL-1α antibody, K-Ras V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, PCR polymerase chain reaction