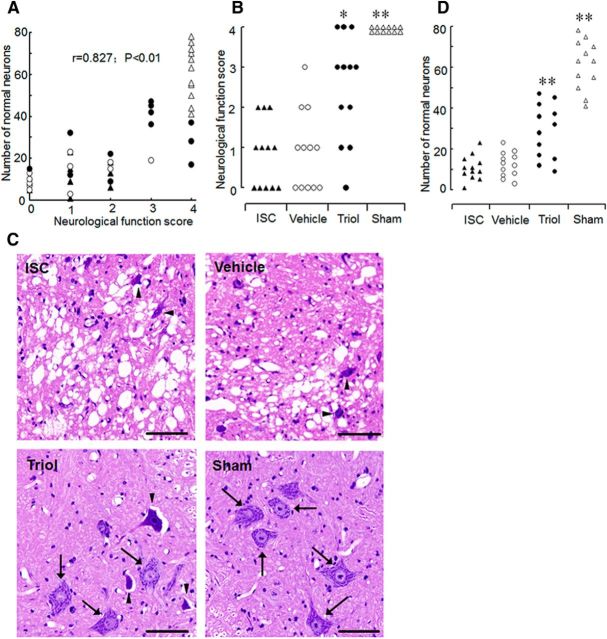
Figure 3.
Neuroprotective effects of triol on spinal cord ischemic injury in rabbit. A, Correlation between the neurological function score and the number of normal neurons in anterior spinal cord 48 h after reperfusion. ▴, ○, ●, and ▵ represent animals in the ischemia, DMSO, triol, and sham groups, respectively. B, Neurological scores of rabbits at 48 h after reperfusion. The ischemia group (ISC), in which the infrarenal aorta was occluded for 20 min to produce spinal cord ischemia injury; the vehicle DMSO group (Vehicle), received intravenous infusion of the same volume vehicle of DMSO; the triol group (Triol), received intravenous infusion of triol with 8 mg/kg 30 min before spinal cord ischemia; the sham group (Sham), underwent exposure of the aorta only. The ISC, vehicle, triol, and sham groups had an average neurological score of 0.83, 0.92, 2.50, and 4.00, respectively. C, Representative results of lumbar spinal cord sections (L5) stained with H&E. Slices were chosen from rabbits rated as having an average score. Note that the darkly stained cytoplasm of dead neurons (arrowheads) compared with the fine granular cytoplasm and Nissl substance of the viable cells (arrows). Scale bars, 50 μm. D, The number of normal neurons of the anterior spinal cord in each animal 48 h after reperfusion. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the ischemia group.