Figure 4.
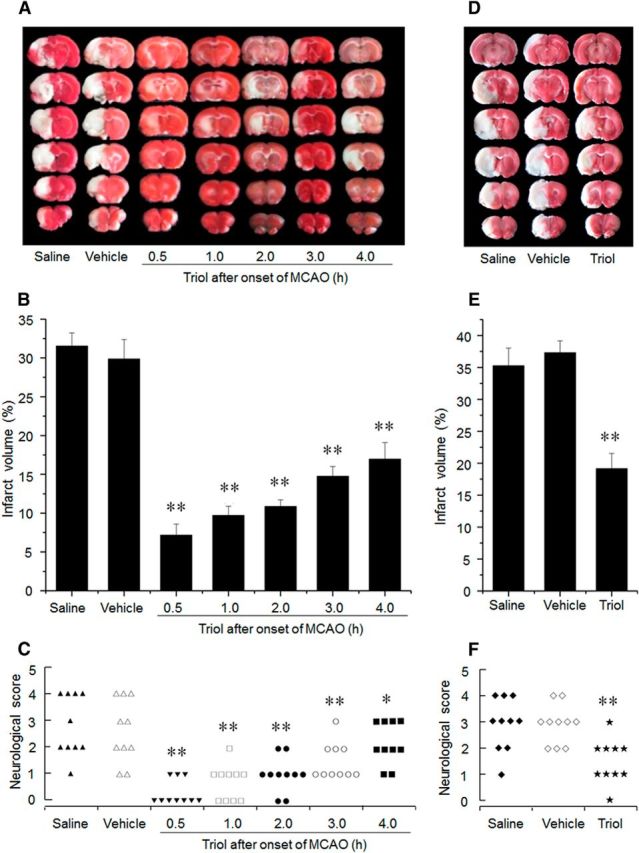
The neuroprotective effects of triol treatment on brain injury induced by MCAO at 24 h and 7 d after reperfusion. A, Representative TTC-stained brain sections at 24 h after reperfusion. Infarction area (pale region) is significantly reduced by intravenous administration of triol (12 mg/kg) at five different therapeutic time windows, respectively, compared with that of the saline or vehicle group. B, Corresponding percentage of infarction volume to the contralateral hemisphere volume at 24 h after reperfusion. The therapeutic time window of triol was used at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 h after onset of MCAO. C, Corresponding neurological outcome of rats at 24 h after reperfusion. D, Representative TTC-stained brain sections at 7 d after reperfusion. Infarction area (pale region) is significantly reduced by intravenous administration of triol (12 mg/kg) at 1 h after onset of MCAO compared with that of the saline or vehicle group. E, Corresponding percentage of infarction volume to the contralateral hemisphere volume at day 7 after reperfusion. F, Corresponding neurological outcome of rats at 7 d after reperfusion. *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.01 compared with the saline group.
