Figure 3. The association between changes in FSWs’ knowledge of HIV status and number of clients from baseline knowledge and sexual behaviours.
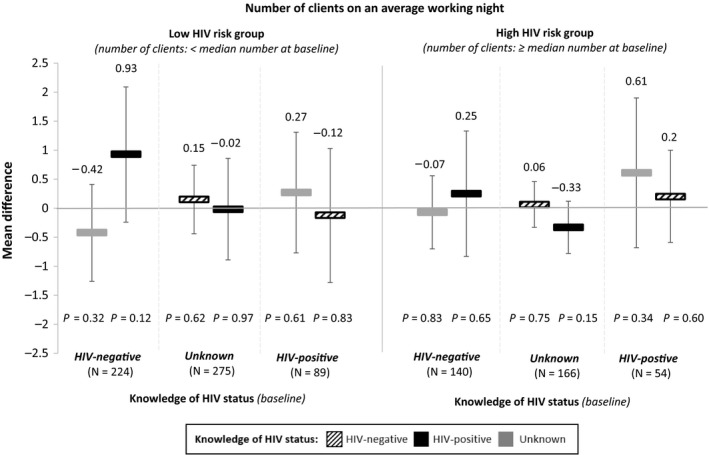
For these sub‐group analyses, participants were sub‐divided by their knowledge of HIV status at baseline and their sexual behaviours at baseline (i.e. low risk vs. high risk). The reference for each sub‐group is participants’ knowledge of HIV status at baseline. The associations between participants’ changing knowledge of HIV and number of clients on an average working night were measured using linear panel regressions with individual fixed effects, controlling for study round (baseline, one month, and four months) and calendar month. Standard errors are adjusted for clustering at the level of the peer educator. The bars show the mean differences in the number of clients for participants whose knowledge of HIV status changed from different states at baseline (listed by sub‐group along the x‐axis) to HIV‐negative (black striped bars), HIV‐positive (black bars), or unknown (grey bars). The vertical lines indicate the 95% confidence intervals.
