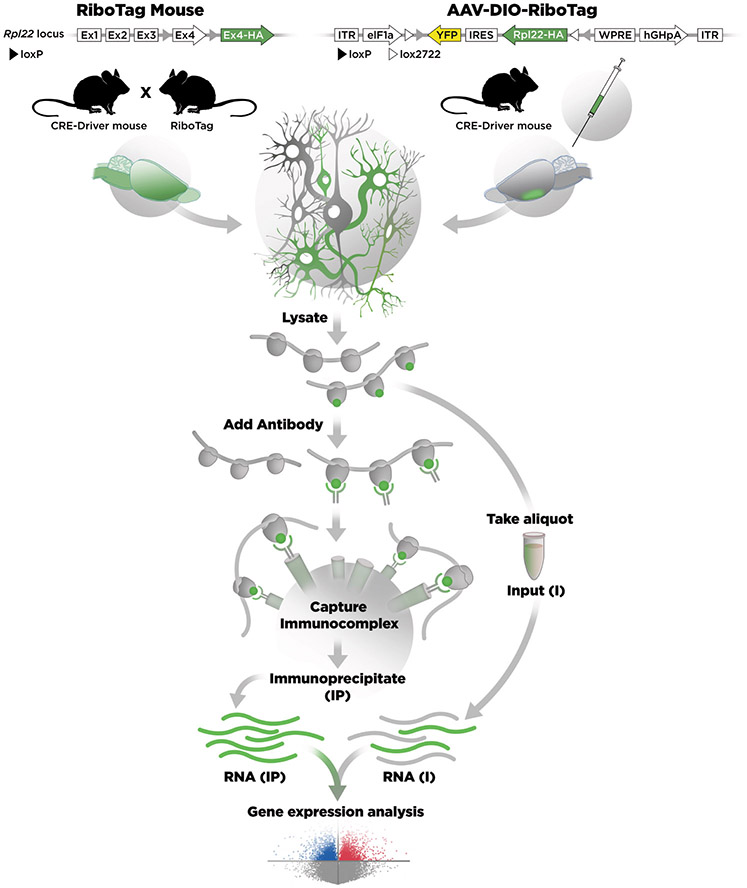
Figure 1. Cartoon comparing the RiboTag mouse and AAV-DIO-RiboTag approaches.
On the left side, the Rpl22 locus was modified by homologous recombination to insert LoxP sites on either end of the last exon (Ex4) of the Rpl22 gene and a duplicated Ex4 with an HA tag was inserted downstream. The CRE-Driver mouse removes the WT Ex4 sequence in specific cells and the transcript now splices in Ex4-HA (shown in green). Polyribosomes from cells expressing the Ex4-HA are recovered from a lysate by immunoprecipitation (IP) with an antibody directed against HA and magnetic beads coated with an artificial Protein A/G peptide. RNA is isolated from the IP polyribosomes and RNA is also isolated from the lysate. Gene expression analysis is done by RNA-Seq. On the right side the DIO-RiboTag viral vector is shown schematically. In the presence of Cre-recombinase the Rpl22-HA-IRES-YFP cassette is flipped and locked in the ON configuration so that the eIF1a promoter now drives expression of Rpl22-HA in specific cells. RNA is isolated from the IP and compared with the input.