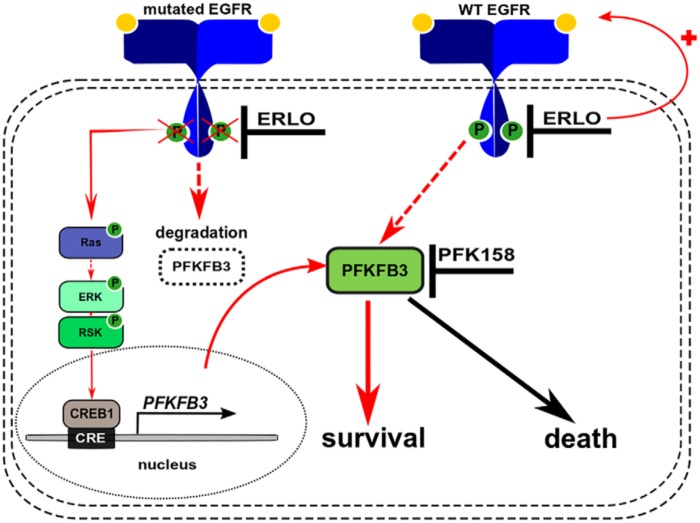
Figure 6.
Model describing the putative mechanism of synergetic interaction between PFK158 and erlotinib in WT and mutEGFR NSCLC cell lines. In mutEGFR cells, chronic inhibition of EGFR signaling by erlotinib promotes reactivation of the MAPK pathway thereby stimulating PFKFB3 transcription via CREB1 binding to the PFKFB3 promoter. Enhanced PFKFB3 transcription compensates for the loss of protein because of targeted degradation by the proteasome and promotes cell survival. In WT-EGFR cells, prolonged erlotinib exposure stimulates EGFR signaling which, in turn, up-regulates PFKFB3 expression by an unknown mechanism and promotes cell survival. PFKFB3 inhibition with PFK158 blocks the prosurvival function of PFKFB3 resulting in a marked increase in cytotoxicity when used in combination with erlotinib. Solid arrows indicate established direct regulations of downstream targets. Dashed arrows indicate indirect activation where intermediate steps are involved but are not specified in this schematic.