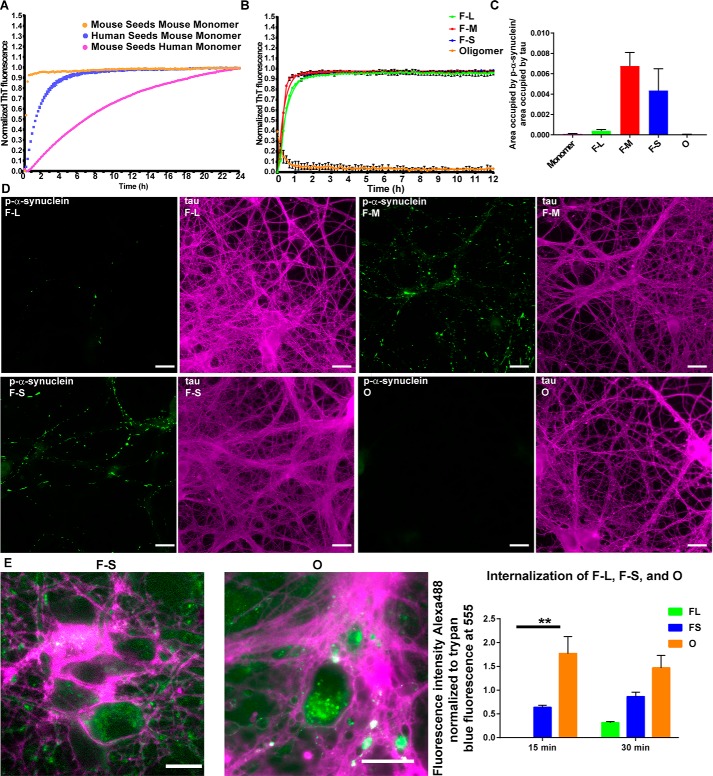
Figure 3.
Seeding ability of the difference assembled forms of α-synuclein species in vitro and in primary neurons. A and B, monomer (100 μm) was incubated with 5 μm fibrillar or oligomeric seeds, and the fluorescence of samples incubated with ThioT was quantified over time. C and D, for the primary hippocampal neurons, 70 nm F-L, F-M, F-S, or oligomers were added to the neurons, and after 7 days, the neurons were fixed, and inclusion formation was visualized using an antibody to p-α-synuclein (green). Immunofluorescence for tau (magenta) shows the distribution of axons (scale bar, 50 mm). ImageJ was used to quantify the percent area occupied by p-α-synuclein fluorescence normalized to the area occupied by tau fluorescence. The data are presented as the mean ± S.E. E, primary hippocampal neurons were preincubated with Alexa488-tagged F-L, F-S or O for 30 min at 4 °C to allow binding to the cell surface. The neurons were then incubated for 15 or 30 min at 37 °C to allow internalization. Fluorescence of external α-synuclein–Alexa488 was quenched using trypan blue. Images show representative α-synuclein–Alexa488 fibrils or oligomers. When trypan blue binds to proteins on the cell surface, it fluoresces at 560 nm, which is shown in the images as magenta (scale bar, 50 μm). The fluorescence intensity of Alexa488 from 10 fields per condition was quantified and normalized to trypan blue immunofluorescence. The internalization experiments were repeated two times. **, p < 0.01.