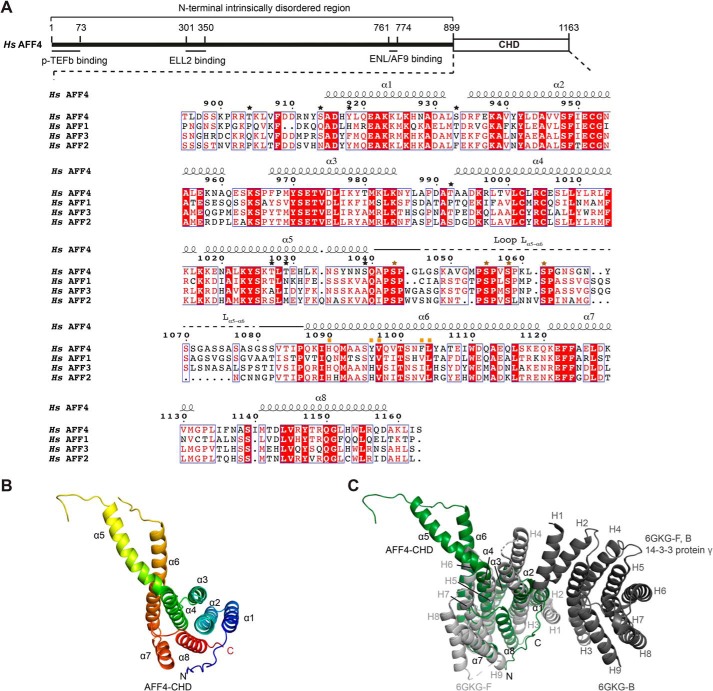
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of the AFF4-CHD. A, scheme of the domain organization of AFF4 and the sequence alignment of human AFF4 (NP_055238.1), AFF1 (NP_001160165.1), AFF3 (NP_002276.2), and AFF2 (NP_001162594.1). The interaction regions of AFF4 with P-TEFb, ELL2, and AF9/ENL are shown as lines under the human AFF4 scheme. The alignment was performed using full-length AFF1, AFF2, AFF3, and AFF4 proteins from human, mouse, chicken, and zebrafish and Lilliputian protein from Drosophila using Jalview (muscle with default) (65). The C-terminal sequences of the human AFF proteins are shown here. The C-terminal sequences of the AFF proteins from all above species are shown in Fig. S1. The secondary structure on top of the alignment was assigned based on the crystal structure of AFF4-CHD to the multisequence alignment using ESPript 3 (66). Stars above the sequences indicate residues that are phosphorylated by P-TEFb identified by MS in this study. Black stars show the residues that are not conserved among AFFs. Brown stars show the phosphorylation sites that are conserved among AFFs. The conserved phosphorylation region Lα5–α6 is marked by solid and dashed lines above the sequence. A dashed line indicates the invisible residues in the crystal structure. Mutated residues on the dimerization interface are marked by orange squares. B, crystal structure of AFF4-CHD in one asymmetry unit. The model is colored from N to C using rainbow colors from blue to red. C, superposition of AFF4-CHD monomer with homodimer of 14-3-3 protein γ (Protein Data Bank code 6GKG-F, B (31)). 14-3-3 protein γ is colored in gray, and AFF4-CHD is colored in dark green as figures above. The α-helices of AFF4-CHD are labeled as α1–α8, and the α-helices of 14-3-3 protein γ are labeled as H1–H9. H1, H3, and H4 of the two 14-3-3 protein γ monomers (in light and dark gray) mediate the homodimerization of 14-3-3 protein γ.