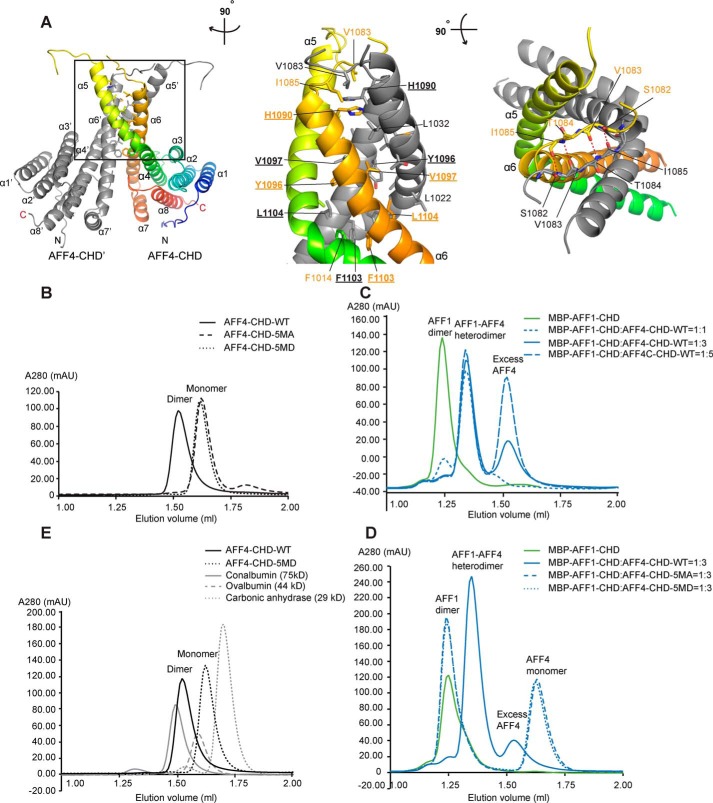
Figure 2.
AFF4-CHD forms homodimer and can form heterodimer with AFF1-CHD in solution. A, dimerization interface of AFF4-CHD homodimer. The left panel shows the overview of the homodimerization interface. In the middle panel, the model is rotated ∼90° clockwise around the vertical axis relative to the overview in the left panel. In the right panel, the model is rotated ∼90° toward the reader around the horizontal axis relative to the view in the middle panel. The two monomers in the dimer are colored gray (AFF4-CHD′) and rainbow (AFF4-CHD), respectively. Residues that are involved in the interface are labeled in orange (AFF4-CHD) and gray (AFF4-CHD′). The side chains (middle panel) or main chains (right panel) are shown as sticks. Underlined letters and numbers indicate residues that are mutated to alanine or aspartate in the 5MA or 5MD constructs for biochemical studies in panels B–D. In the right panel, red dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. B, disruption of the dimerization interface abolished the homodimerization of AFF4-CHD. The state of WT and mutants (5MA and 5MD) of AFF4-CHD are analyzed by analytical gel filtration. The elution profiles of WT and mutants of AFF4-CHD are shown as smoothed lines. The raw data were exported from UNICORN and plotted as smoothed lines in Excel. AFF4-CHD–5MA contains the following mutations: H1090A, Y1096A, V1097A, F1103A, and L1104A. AFF4-CHD–5MD contains mutations H1090D, Y1096D, V1097D, F1103D, and L1104D. The WT, 5MA, and 5MD elution profiles are shown in solid, dashed, and dotted black lines, respectively. C, WT AFF4-CHD forms a heterodimer with MBP–AFF1-CHD. The elution profiles of MBP–AFF1-CHD and premixed MBP–AFF1-CHD/AFF4-CHD are shown as smoothed lines. MBP–AFF1-CHD alone (in green) serves as a control. To form the AFF4-CHD/AFF1-CHD complex, AFF4-CHD and MBP–AFF1-CHD were mixed in different ratios (1:1, 1:3, and 1:5 molar ratios) and incubated overnight at 4 °C. The protein mixtures were sequentially injected onto analytical gel filtration column, and the profiles of the preincubated MBP–AFF1/AFF4 protein at different ratios are presented as solid (1:3) and dashed blue lines (1:1 and 1:5) as indicated in the figure. D, the AFF4-CHD mutants failed to form heterodimers with MBP–AFF1-CHD. The MBP–AFF1-CHD are premixed with AFF4-CHD–WT or AFF4-CHD mutants (5MA and 5MD) in 1:3 ratio and incubated overnight prior injection to analytical gel filtrations. The MBP–AFF1-CHD alone (in green) serves as a control. Solid, dashed, and dotted blue lines indicate the elution profile of MBP–AFF1-CHD premixed WT, 5MA, and 5MD, respectively. E, comparison of the molecular mass of AFF4-CHD–WT and 5MD with size exclusion standards. The elution profiles of AFF4-CHD–WT, AFF4-CHD–5MD, and size exclusion standards including conalbumin, ovalbumin, and carbonic anhydrase are shown as a black solid line, a black dashed line, a gray solid line, and a gray dashed line, respectively.