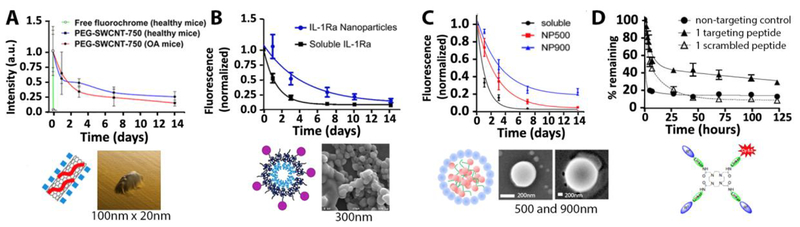
Figure 2.
Whole joint retention profiles across different nanomaterials (above) with a variety of structures, compositions, sizes, and shapes (below). In all cases, retention is presented as fluorescence intensity normalized the signal intensity immediately after injection. (A-C) Studies that include a soluble fluorophore show that joint retention is prolonged by nanomaterials within two weeks. (D) Incorporating a collagen type II binding peptide for cartilage targeting also slowed whole joint release. (A) PEG-based nano-tube [74]1, (B) tri-block polymeric nanoparticle [75]2, (C) self-assembling polymeric nanoparticle [76]3, (D) DOTAM carrier molecule [77]4. Figures reprinted with permission (see footnotes). DOTAM = 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid amide; IL-1Ra = Interluekin-1 receptor antagonist; PEG-SWCNT-750 = polyethylene glycol single-walled carbon nanotubes (with a 750nm emitting fluorochrome); NP500 or NP900 = Nanoparticle of 500nm or 900nm.