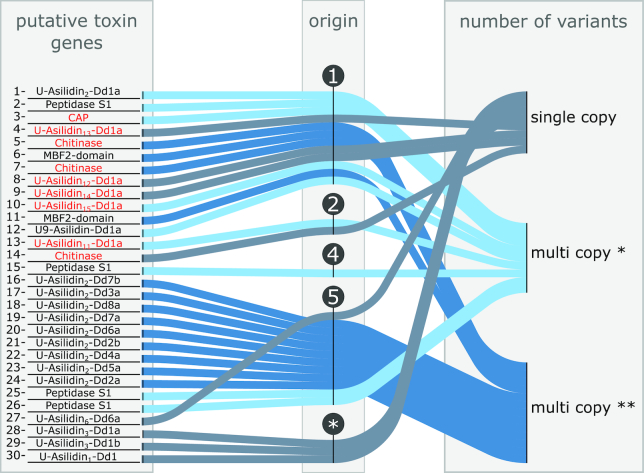
Fig. 4:
The evolutionary pattern and the origin of the top 30 putative toxins. The node numbering refers to the nodes in Fig. 3a. Putative toxins present in Dasypogon diadema but missing in Eutolmus rufibarbis or Machimus arthriticus are coloured red. Single-copy genes: putative toxins with only 1 copy on the protein-coding genome of D. diadema; multi-copy genes*: protein-coding genes that belong to orthogroups assembled of ≥2 protein-coding genes in D. diadema. Only 1 member of the orthogroup is present in the venom; multi-copy genes**: protein-coding genes that belong to orthogroups assembled of ≥2 protein-coding genes in D. diadema. Two or more members of the same orthogroup are present in the venom.