Figure 4. C3 deposition on NKAP-deficient naïve T cells requires both the lectin and classical pathways.
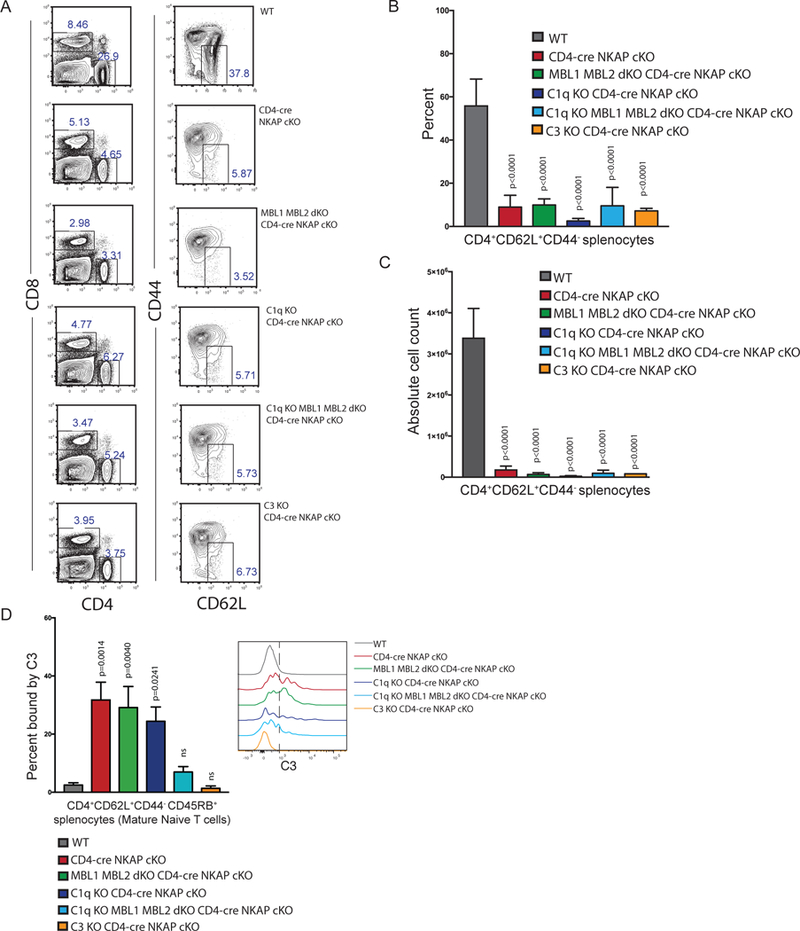
(A) Representative frequencies of CD4+ and CD4+CD62L+CD44− splenocytes in WT, CD4-cre NKAP cKO, MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, and C3 KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO mice. (B, C) Enumeration of absolute cell counts and frequencies of CD4+CD62L+CD44− splenocytes in WT, CD4-cre NKAP cKO, MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, and C3 KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO mice. (D) Enumeration of frequencies of CD4+CD62L+CD44−CD45RB+ mature naïve splenocytes bound by C3 from WT, CD4-cre NKAP cKO, MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, C1q KO MBL1 MBL2 dKO CD4-cre NKAP cKO, and C3 KO CD4-cre NKAP cKO mice. All data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments with at least 6 mice per genotype in total. P-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. Error bars for all figures represent SEM.
