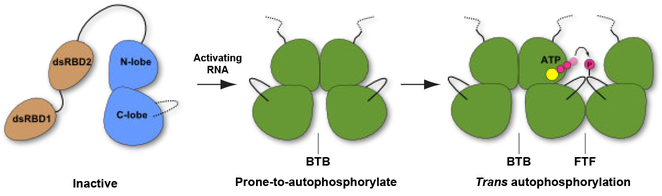
Figure 7. Multistep model for PKR activation.
The kinase domain of monomeric PKR exists in an inactive conformation. In the first step, PKR binds to activating RNAs via the tandem dsRBDs (dsRBD1 and dsRBD2), bringing two kinase domains into proximity to promote dimerization. Formation of the BTB dimer stabilizes the prone-to autophosphorylate-conformation. In the second step, the BTB dimer phosphorylates the activation loop of a PKR monomer docked in a domain-swapped, FTF geometry. The kinase domain in the inactive conformation is depicted in blue and the prone-to-autophosphorylate and active conformations are shown in green.