Figure 3.
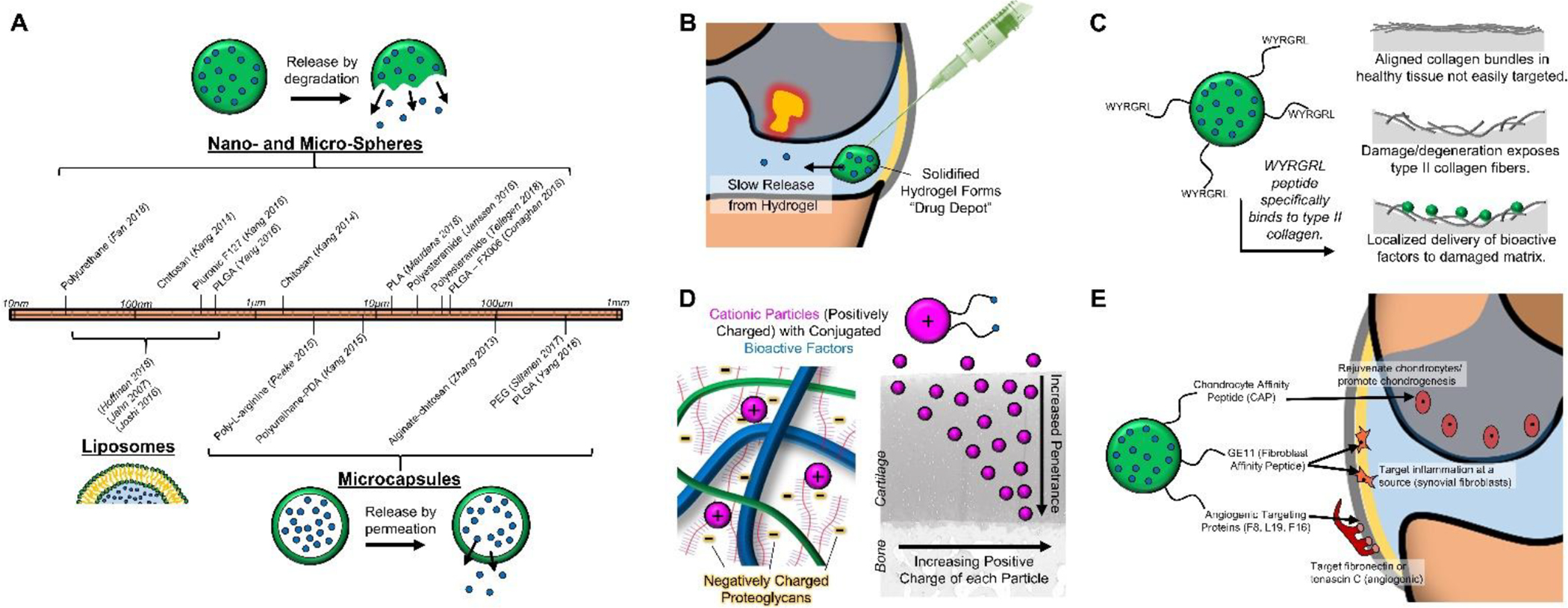
Intra-articular Drug Delivery Systems. [A] Materials used for nano- and micro-spheres, liposomes, and microcapsules span a wide range of sizes (10nm – 1mm). [B] Hydrogel “drug depots” can extend drug release within the joint. [C] Targeting molecules (e.g. WYRGRL) can focus delivery to the damaged cartilage interface. [D] Cationic particles can increase penetrance for improved drug delivery within cartilage tissue. [E] Drug delivery vehicles can target specific cells and structures (e.g. chondrocytes, synovial fibroblasts, angiogenic regions).
