Figure 5.
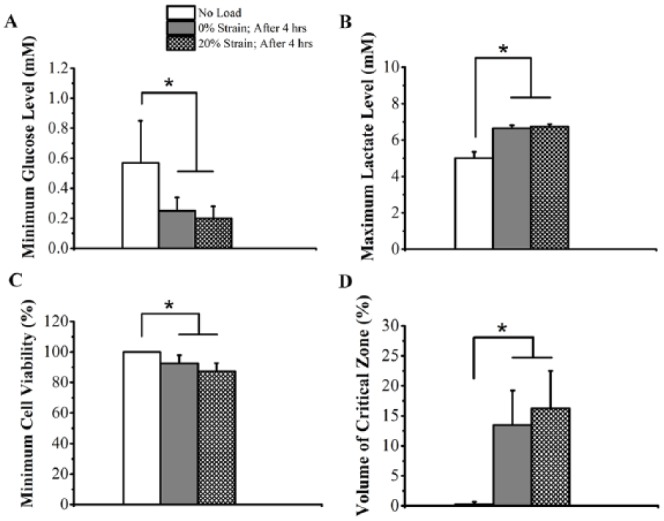
Effect of mechanical loading on (A) minimum glucose level, (B) maximum lactate level, (C) minimum cell viability, and (D) volume of critical zone in temporomandibular joint (TMJ) discs from 11 human subjects. “No load”: unloaded TMJ disc; “0% Strain; After 4 h”: solute diffusivities collected under 0% strain level were used for the whole TMJ disc; “20% Strain; After 4 h”: solute diffusivities collected under 20% strain level were used for the loaded disc region. The solute diffusion through the superior and inferior loading surfaces of the TMJ disc was blocked for 4 h. *P < 0.05. Sample size: n = 11 human TMJ discs in 11 healthy human male volunteers.
