Figure 2.
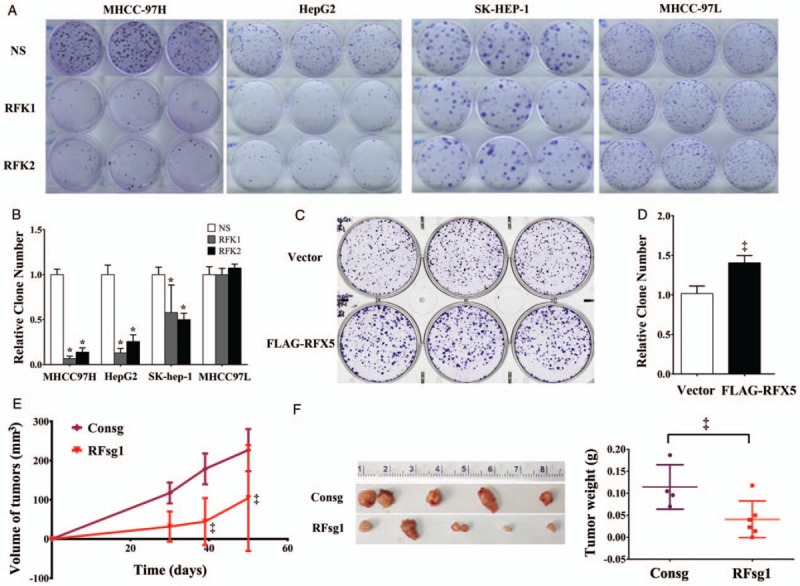
Oncogene dependence of RFX5 in HCC. (A and B) Clonogenicity assay of MHCC-97H, HepG2, SK-HEP-1 and MHCC-97L infected with lentiviral control shRNA (NS) and RFX5 specific shRNAs (RFK1 and RFK2) (A) and the quantification of colonies of four HCC cell lines from three independent repeats. Data were shown as mean ± SD (B). (C and D) Clonogenicity assay of HepG2 cells infected lentivirus Vector and FLAG-RFX5 (C), and the quantification of clone numbers from three independent repeats. Data were shown as mean ± SD (D). (E and F) MHCC-97H cells treated with lentivirus expressing espCas9 and sgRNAs against non-targeting control (Consg) and RFX5 (RFsg1) were subcutaneously implanted in BALB/c Nude. Tumor volumes were measured with calipers and calculated (E). Tumors were harvested and weighted after MHCC-97H implantation for 50 days (F). ∗P < 0.001, ‡P < 0.05. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RFX5: Regulatory factor X-5; SD: Standard deviation; shRNA: Short hairpin RNA.
