Figure 9.
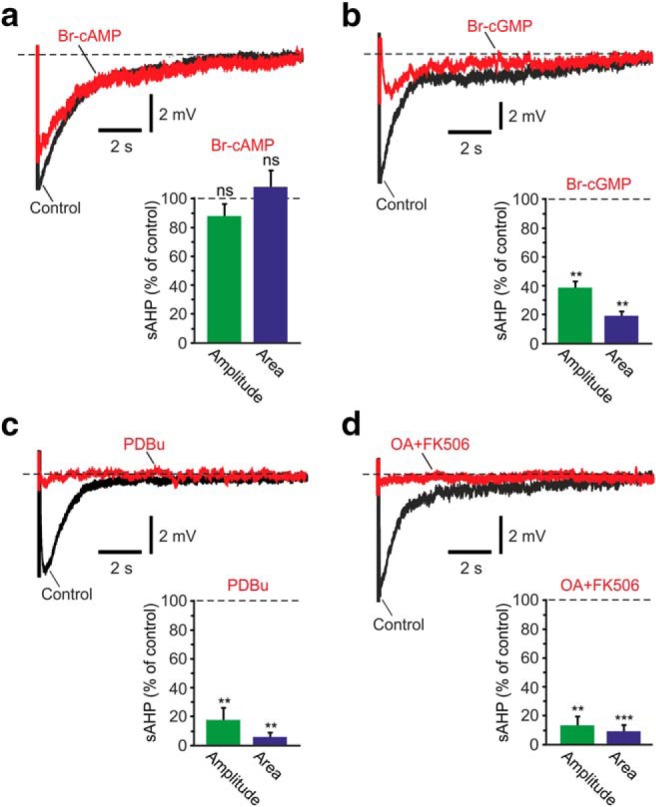
NKA-sAHPs evoked by Na+ injections are regulated by PKs and PPs. a, NKA-sAHPs were evoked by intracellular Na+ injections in TTX-containing aCSF. Activation of PKA: The two overlaid traces represent the NKA-sAHPs in the same neuron before (black) and after perfusing the slice with the PKA activator Br-cAMP (2 mm; red). Bar represents the normalized results of four experiments (mean ± SEM) for NKA-sAHP amplitudes (green) and areas (blue). b, Activation of PKG: Same as in a, but applying the PKG activator Br-cGMP (100 μm; n = 4). c, Activation of PKC: Same as in a, but applying the PKC activator PDBu (5 μm; n = 5). d, Inhibition of PPs. Same as in a, but applying the PP inhibitors OA (1 μm) and FK506 (10 μm; n = 4). Activation of PKA had no significant effect on the NKA-sAHPs, whereas all other treatments strongly suppressed these potentials, implicating PKG, PKC, and the PPs in NKA activity regulation by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, not significant.
