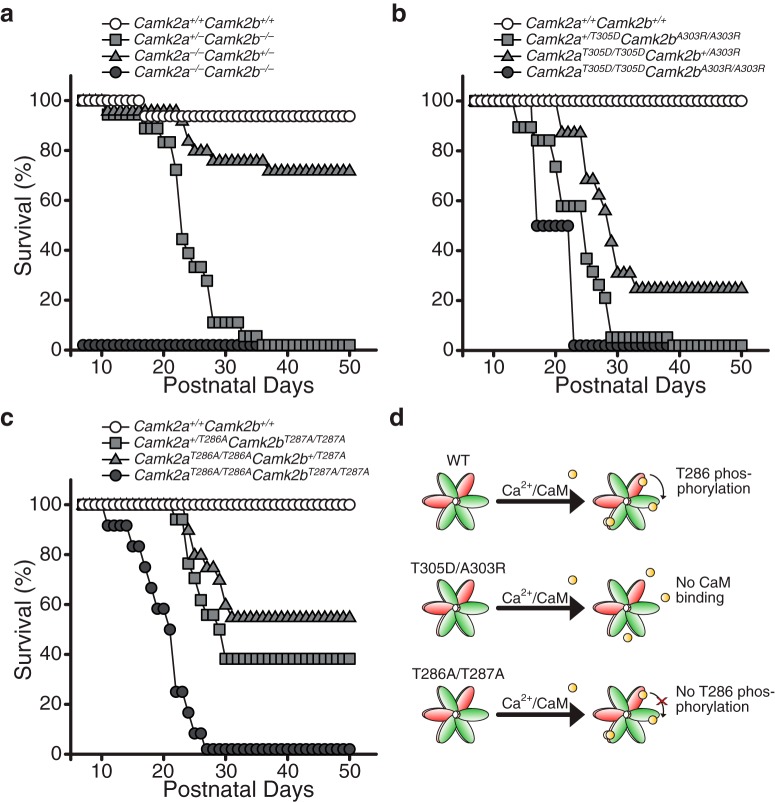
Figure 1.
Multiple Camk2a mutants crossed with Camk2b mutants and their survival in percentage of their total group size. a, Double knock-out mice for both Camk2a and Camk2b (Camk2a−/−;Camk2b−/−) die on P0. Homozygosity for Camk2b (with 1 functioning allele of Camk2a: Camk2a+/−;Camk2b−/−, n = 18) has a more severe impact on survival than homozygosity for Camk2a (and 1 functioning allele of Camk2b: Camk2a−/−;Camk2b+/−, n = 25). Camk2a+/+;Camk2b+/+ were used as controls (n = 16). b, Homozygous loss of Ca2+-dependent activity of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B (Camk2aT305D/T305D;Camk2b;A303R/A303R, n = 2) results in early death. Homozygosity for a A303R knock-in mutation in Camk2b and a heterozygous T305D knock-in mutation for Camk2a (Camk2a+/T305D;Camk2bA303R/A303R, n = 18) has a more severe impact on survival than a homozygous knock-in mutation for Camk2a and a heterozygous A303R knock-in mutation for Camk2b (Camk2aT305D/T305D;Camk2b+/A303R, n = 15). Camk2a+/+;Camk2b+/+ were used as controls (n = 4). c, Homozygous loss of autonomous activity of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B (Camk2aT286A/T286A;Camk2bT287A/T287A, n = 12) results in early death. Again, homozygosity for a T287A knock-in mutation in Camk2b (and a heterozygous T286A knock-in mutation for Camk2a: Camk2a+/T286A;Camk2bT287A/T287A, n = 34) has a more severe impact on survival than a homozygous knock-in mutation for Camk2a (and a heterozygous T287A knock-in mutation for Camk2b: Camk2aT286A/T286A;Camk2b+/T287A, n = 20). Camk2a+/+;Camk2b+/+ were used as controls (n = 14). With the exception of one mouse in the first experiment (a), all Camk2a+/+;Camk2b+/+ mice survived a minimum of up to 50 d postnatally. d, Model showing the effect of the different mutations used on the activity of the holoenzyme for the survival experiments. Green, CAMK2A; red, CAMK2B; yellow, calcium/calmodulin.