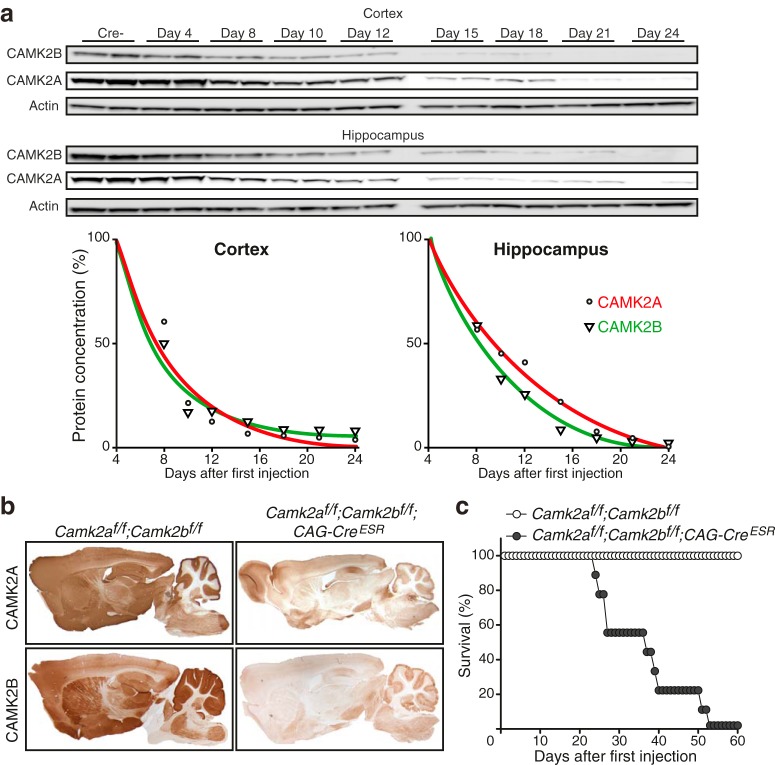
Figure 2.
Adult loss of CAMK2A and CAMK2B is lethal. a, Western blot of cortical (top) and hippocampal (bottom) lysates using antibodies targeted against CAMK2A and CAMK2B. Actin was used as loading control. Days after first injection are indicated above the blots. Cre- mice were killed 4 d after the first tamoxifen injection. Bottom left graph, Nonlinear regression curve showing protein degradation in cortex, showing no difference in protein degradation rate of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B (n = 2 for each time point). Bottom right graph, Nonlinear regression curve showing protein degradation in hippocampus, where CAMK2B degradation is faster than CAMK2A degradation. Comparing both graphs, protein degradation of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B is faster in the cortex than in the hippocampus. b, Immunohistological stainings showing effective loss after tamoxifen injections of CAMK2A (top) and CAMK2B (bottom) in Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice 21 d after onset of gene deletion. c, Loss of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B (Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR) in adulthood is lethal. Both groups of mice [Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR (n = 9) and Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f (n = 8)] received tamoxifen injections (see Materials and Methods).