Figure 5.
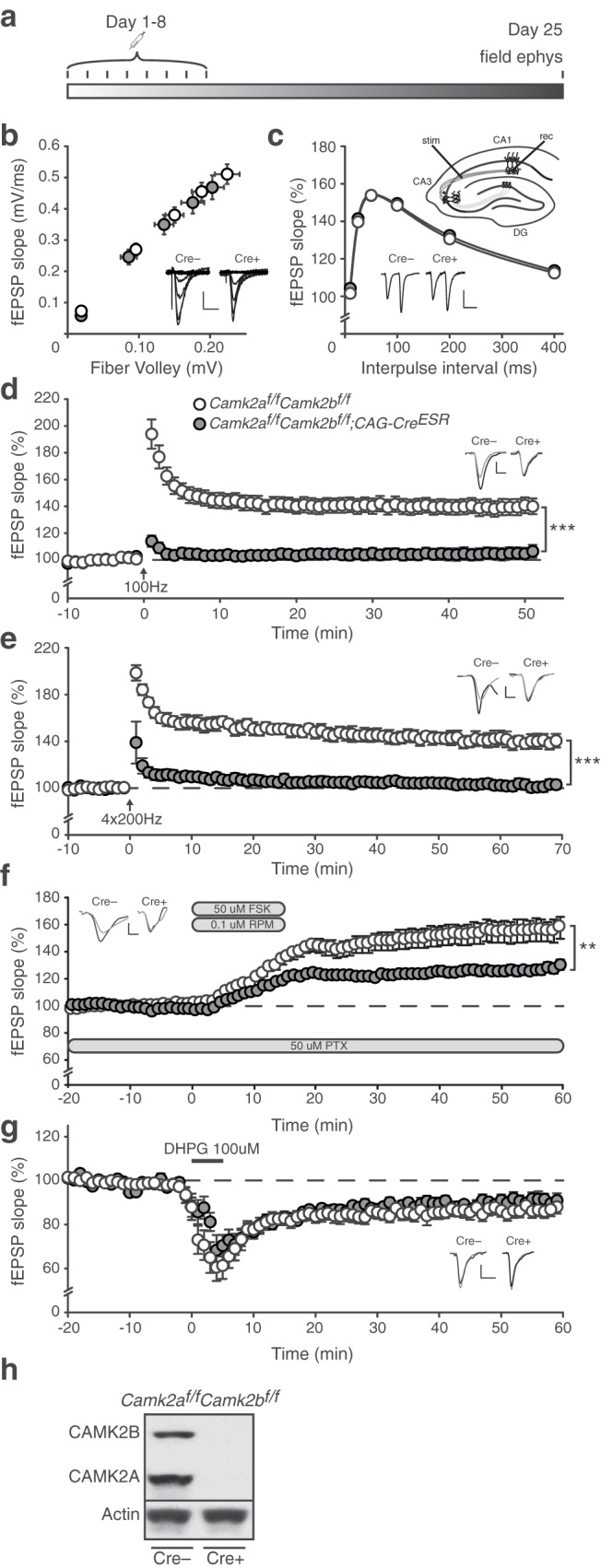
CAMK2A and CAMK2B are essential for CA3–CA1 LTP. a, Timeline showing the loss of CAMK2A and CAMK2B upon induction of genomic deletion with Tamoxifen injections (see Materials and Methods). Mice were killed 25 d after the first injection to conduct electrophysiological experiments. b, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice [fiber volley: (n = 30 from 11 mice), fEPSP slope: (n = 42 from 11 mice)] show normal basal synaptic transmission compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice [fiber volley: (n = 29 from 15 mice), fEPSP slope: (n = 50 from 15 mice)]. c, Inset, Schematic overview of LTP induction in the CA3–CA1 pathway (see Materials and Methods). stim, Stimulating electrode; rec, recording electrode; DG, dentate gyrus. Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice (n = 40 from 11 mice) show normal PPF compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice (n = 51 from 15 mice). d, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice (n = 16 from 6 mice) show a complete loss of 100 Hz LTP compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice (n = 21 from 9 mice). e, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice (n = 11 from 4 mice) show a complete loss of 200 Hz LTP compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice (n = 9 from 5 mice). f, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice (n = 28 from 7 mice) show impaired forskolin/rolipram-induced (50 μm/0.1 μm) LTP compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice (n = 29 from 7 mice). FSK, Forskolin; RPM, rolipram; PTX, picrotoxin. g, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice (n = 9 from 5 mice) show normal DHPG-induced (100 μm) LTD compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice (n = 13 from 6 mice). h, Western blot showing efficient loss of both CAMK2A and CAMK2B in the acute hippocampal slices of Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CAG-CreESR mice with normal CAMK2A and CAMK2B expression in Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice. Actin levels are shown as loading control. Error bars indicate SEM. Electrophysiological example traces can be found within the figures. Scale bars: y, 0.2 mV; x, 10 ms. **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0001.
