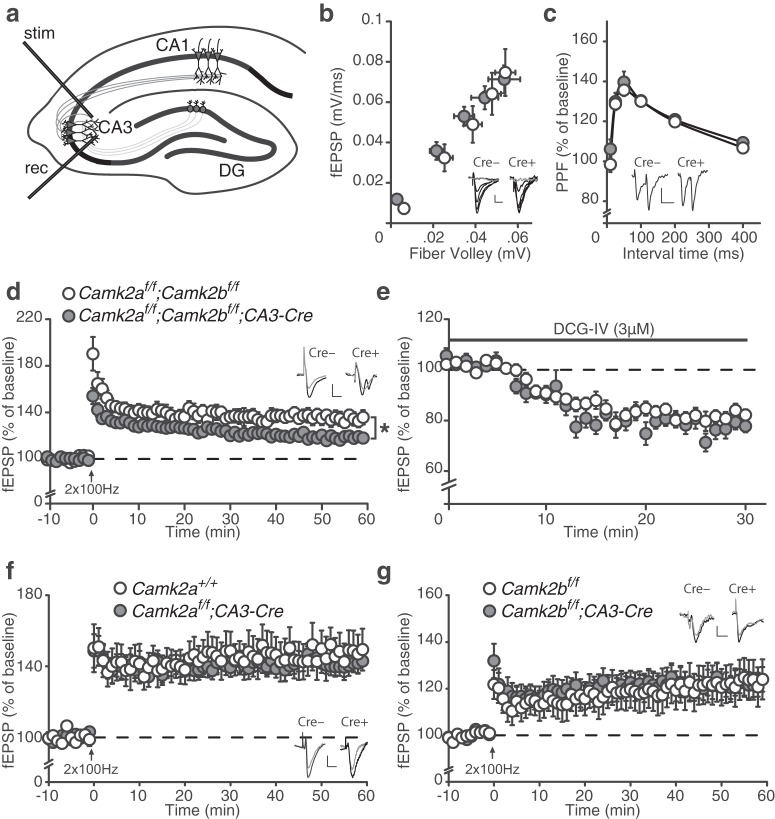
Figure 7.
Redundancy of CAMK2A and CAMK2B in CA3–CA3 LTP. a, Schematic overview of LTP induction in the CA3–CA3 pathway (see Materials and Methods). stim, Stimulating electrode; rec, recording electrode; DG, dentate gyrus. b, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CA3-Cre mice [fiber volley: (n = 27 from 4 mice), fEPSP slope: (n = 23 from 4 mice)] mice show normal basal synaptic transmission compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f mice [fiber volley: (n = 24 from 4 mice) fEPSP slope: (n = 24 from 4 mice)]. c, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CA3-Cre (n = 17 from 4 mice) mice show normal PPF compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f (n = 21 from 4 mice) mice. d, Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CA3-Cre (n = 16 from 4 mice) show reduced 100 Hz LTP compared with Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f (n = 18 from 4 mice) mice. e, DCG-IV only minimally blocks the fEPSP signal in both Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f;CA3-Cre (n = 21 from 4 mice) and Camk2af/f;Camk2bf/f (n = 21 from 4 mice) mice. f, Camk2af/f;CA3-Cre (n = 29 from 8 mice) show normal 100 Hz LTP compared with Camk2a+/+ (n = 16 from 5 mice) mice. g, Camk2bf/f;CA3-Cre (n = 28 from 8 mice) show normal 100 Hz LTP compared with Camk2bf/f (n = 24 from 8 mice) mice. Error bars indicate SEM. Electrophysiological example traces can be found within the figures. Scale bars: y, 0.1 mV; x, 10 ms. *p = 0.01