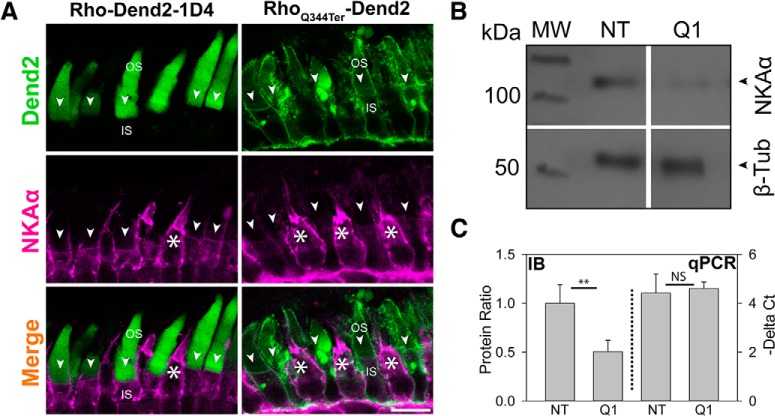
Figure 3.
NKAα is downregulated in rods expressing RhoQ344ter-Dend2. A, Immunofluorescence labeling of NKAα (magenta) in retinas expressing either Rho-Dend2-1D4 (left column) or RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (right column). NKAα signal on the PM of cells expressing wild-type rhodopsin was relatively uniform (Rho-Dend2-1D4, NKAα, arrowheads), whereas the NKAα signal was noticeably reduced or absent from cells expressing class I mutant rhodopsin (RhoQ344ter-Dend2, NKAα, arrowheads). NKAα expression was robust in cone cells (white asterisks). B, Representative immunoblot comparing the expression levels of NKAα and β-tubulin in NT or Q1 retinas. Molecular weight (MW) is indicated in kilodaltons. C, Left side of graph (IB, delimited by dotted line): in NT or Q1 retinas, the protein amounts of NKAα were quantified and normalized to the amounts of β-tubulin protein. NT value was standardized to 1.00. (Exact values were 1.00 ± 0.0.19 for NT and 0.50 ± 0.12 for RhoQ344ter-Dend2, based on n = 6 animals; p < 0.01). Right side of graph (qPCR): the amount of NKAα transcript relative to β-tubulin transcript was assessed by quantitative PCR. ΔCt values of nontransgenic and high-expression RhoQ344ter-Dend2 retinas were compared (4.60 ± 0.27 for RhoQ344ter-Dend2 retinas and 4.42 ± 0.78 for nontransgenic retinas based on n = 5 animals; p = 0.63). Scale bar, 10 μm. **p < 0.01, NS, not significant.