Figure 4.
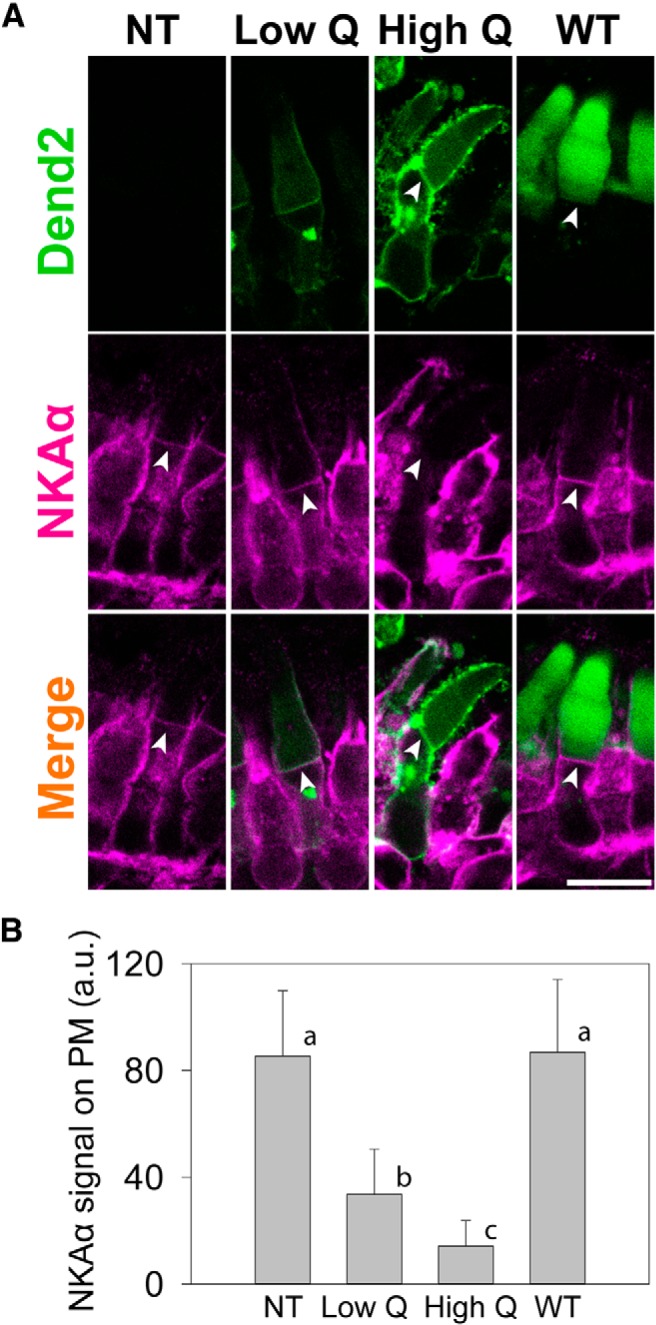
Degree of NKAα downregulation is dependent on the amount of class I mutant rhodopsin. A, Direct comparison of NKAα immunofluorescence in a rod cell not expressing RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (NT), a rod cell expressing low amount of RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (Low Q), a rod cell expressing high amount of RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (High Q), and a rod cell expressing Rho-Dend2-1D4 (WT). Arrowheads indicate the apical region of the IS PM. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Quantification of NKAα immunofluorescence observed in A. Compared with NT and WT rods, NKAα was downregulated in rods expressing class I mutant rhodopsin in a manner depending on the expression level of RhoQ344ter-Dend2. Rods with low expression of RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (Low Q) had higher quantities of NKAα on the PM than rods with high expression of RhoQ344ter-Dend2 (High Q). By ANOVA Tukey post hoc test, all the pairs (a vs b, a vs c, and b vs c) were significantly different (p < 0.001; based on 52 cells from n = 4 animals for each condition) except for between WT and NT rods (a, p = 0.58), which indicated that the presence of the wild-type rhodopsin transgene did not affect the expression of NKAα.
