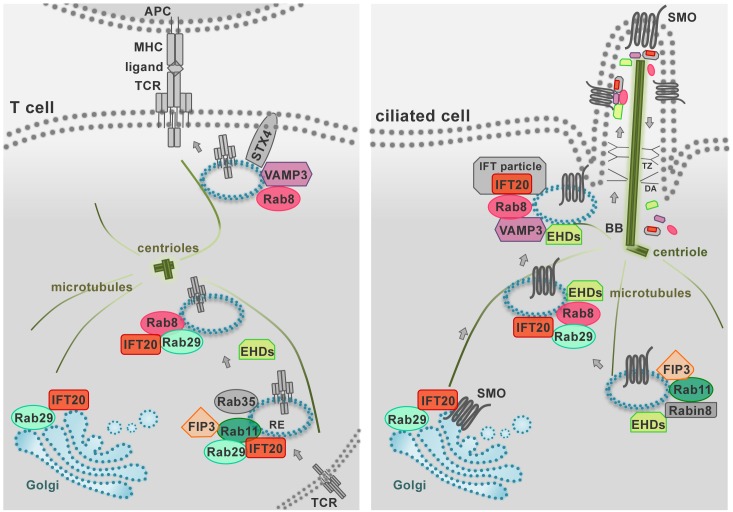
FIGURE 3.
The endosomal trafficking pathways that control protein targeting to the primary cilium are co-opted by T cells for immune synapse assembly. The IS (left) represents the functional homolog of the primary cilium in the non-ciliated T cell (right) as these specialized structures share both structural properties and signaling pathways. During IS and primary cilium formation the centrioles and Golgi apparatus polarize beneath the respective signaling membrane domains. In addition, the polarized delivery of the T-cell receptor (TCR) and ciliary receptors (e.g., SMO, Smoothened) require common vesicular trafficking pathways coupling a recycling endosomal pool (marked by IFT20, Rab11, Rab29, FIP3) to the vesicle pool docked at the IS or at the primary cilium (marked by Rab8 and VAMP3). Notably, in ciliated cells IFT proteins shuttle cargo to the cilium and back to the cell body as large multimolecular complexes, known as IFT particles. In T cells, all the subunits of the IFT particles are expressed and IFT20 interacts with the IFT proteins IFT88, IFT57, and IFT52 (not shown) to promote TCR recycling to the IS. Similarly, a novel role of the EHD proteins in TCR trafficking has been recently described beyond their well-known function in ciliated cells. Shared traffic regulators are shown in color, other regulators in gray. BB, basal body; DA, distal appendages; RE, recycling endosome; TZ, transition zone.