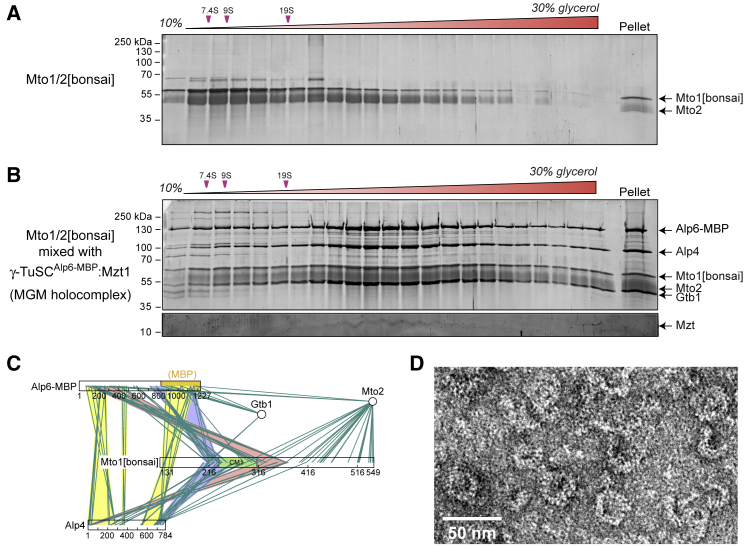
Figure 2.
γ-TuSC:Mzt1 Interacts with Mto1/2[bonsai] Complex to Form An “MGM” (Mto/Gamma/Mzt) Holocomplex
(A) SDS-PAGE of 80-min density-gradient centrifugation of Mto1/2[bonsai].
(B) SDS-PAGE of 80-min density-gradient centrifugation of Mto1/2[bonsai] mixed (after purification) with γ-TuSCAlp6-MBP:Mzt1. Mixing alters the sedimentation profiles of both complexes, and all constituent proteins cosediment. Mzt1 was visualized on a separate gel with higher acrylamide concentration. Gels are stained with SYPRO Ruby. Representative sedimentation profiles from (A) and (B) are shown in Figure S2A.
(C) Interactions between different proteins within MGM holocomplex, identified by zero-length chemical crosslinking and mass spectrometry (see STAR Methods). For simplicity, only interprotein crosslinks are shown. In this experiment, crosslinks to Mzt1 (a very small protein with few useful proteolytic fragments) were not identified.
(D) Negative-stain electron microscopy of MGM. The image is a portion of a field shown in Figure S2F. In (C) and (D), MGM was purified from coexpression of Mto1/2[bonsai] and γ-TuSCAlp6-MBP:Mzt1 proteins.