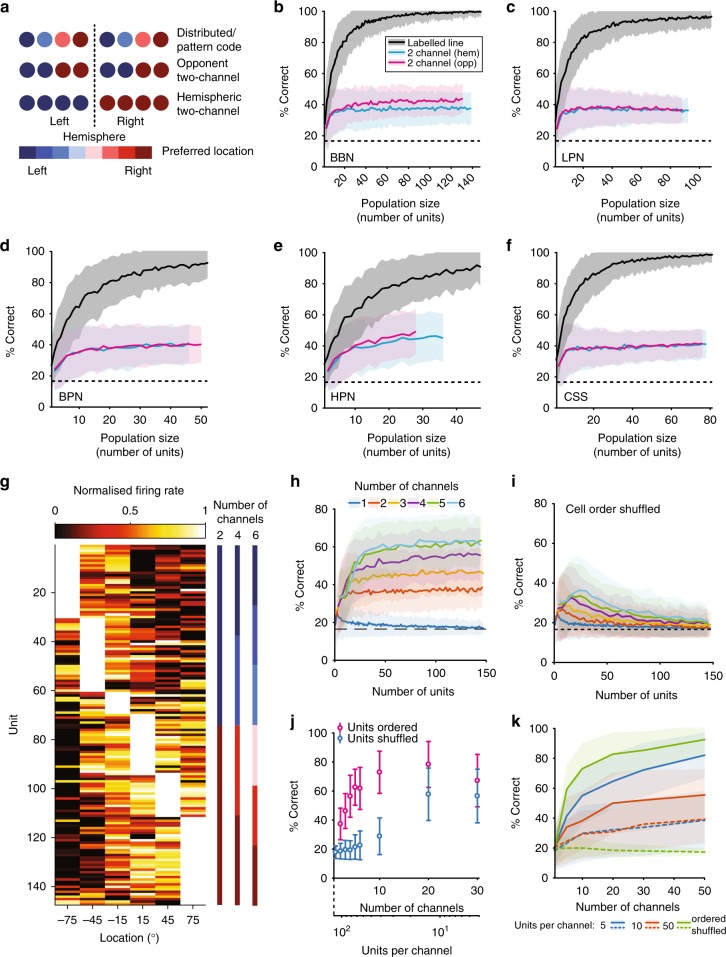
Fig. 7.
Distributed model population decoding outperforms two-channel models. a Schematic of three possible spatial coding mechanisms. b–f Performance of the two-channel (hemispheric–blue, opponent–magenta) and distributed (grey) decoders in each stimulus condition from populations of neurons that had significant MI about location. Performance of each decoder was calculated as percentage of correctly classified individual trials. The dotted line indicates chance (1/6). The black line and coloured bands indicate the mean ± s.d. of the performance for 250 different random subpopulations of each size drawn from the full sample of cells. g Spatial receptive fields for all units used in the population analysis for BBN, ordered by best position. h Decoder performance for models with increasing channel numbers with units grouped according to g. i Decoder performance when units are randomly ordered and assigned to channels. j Comparison of decoder performance and shuffled performance for a fixed population of 120 cells divided into increasing numbers of channels. k Effect of the number of units per channel using the data from modelled unit responses for ordered and shuffled units (see the Methods)