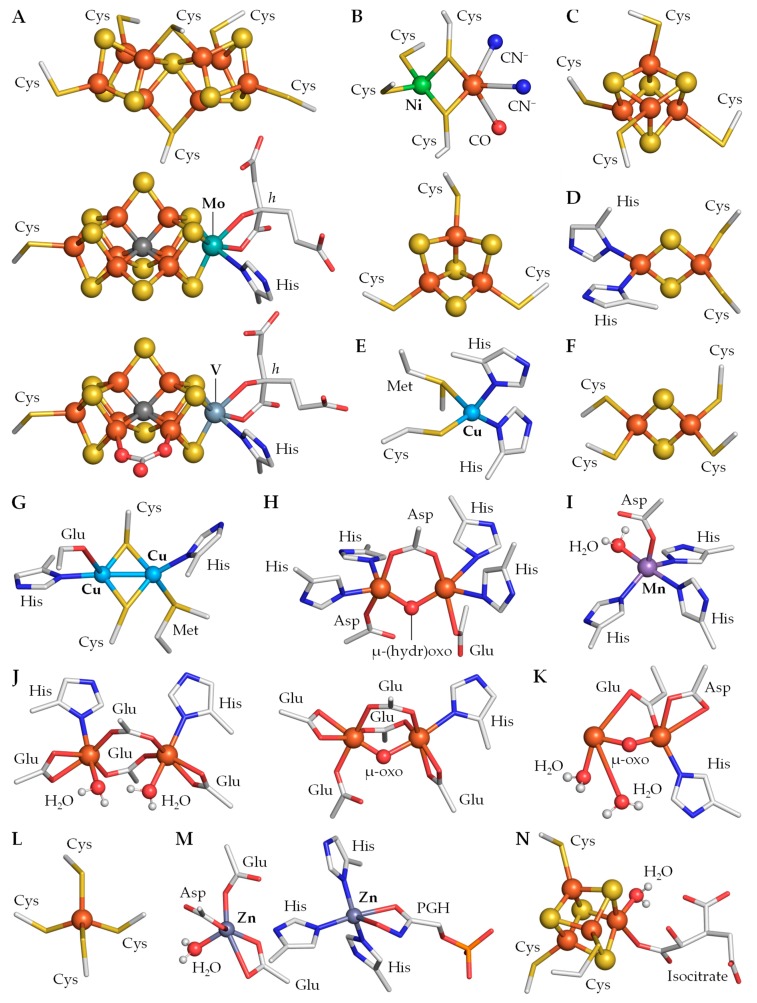
Figure 2.
Representative metal clusters in heterocyst metalloproteins. (A) P cluster (top) and FeMo-co (middle; Mo nitrogenase, 4wza), and FeV-co (bottom; V nitrogenase, 5n6y). (B) Ni–Fe (top) and [3Fe–4S] (bottom) clusters (Ni–Fe hydrogenase, 3rgw). (C) [4Fe–4S] cluster FB (photosystem I, 6hqb). (D) Rieske cofactor (cytochrome b6f, 4ogq). (E) Cu center (plastocyanin, 2cj3). (F), [2Fe–2S] cluster (ferredoxin FdxH, 1frd). (G) Cu–Cu center CuA (cytochrome c oxidase, 1qle). (H) Fe–Fe center (flavodiiron protein, 1ycf). (I) Mn center (Mn SOD, 1gv3). (J) reduced (left) and oxidized (right) Fe–Fe center (rubrerythrin, 1lko/1lkm). (K) Fe–Fe ferroxidase center (Dps protein, 1n1q). (L) [Fe–4S] cluster (rubrerythrin, 1lko). (M) Zn centers bound to the substrate analogue phosphoglycolohydroxamate (PGH; fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase, 1b57). (N) catalytic [4Fe–4S] cluster bound to isocitrate (aconitase, 1b0j). h, homocitrate.