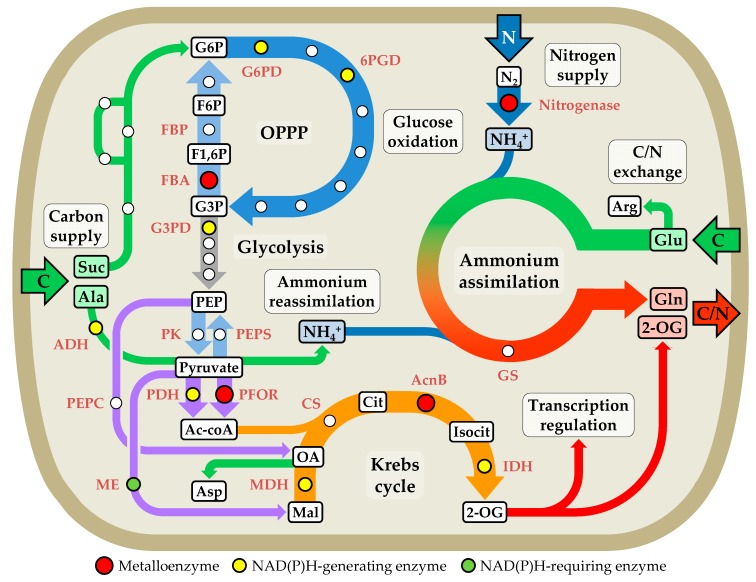
Figure 5.
Main energy metabolism and carbon/nitrogen fluxes in heterocysts. The OPPP (oxidative pentose phosphate pathway) and the Krebs cycle are the major routes used by heterocysts to generate reducing equivalents, while glycolysis has a smaller contribution. Metalloenzymes (red circles) and enzymes catalyzing reactions that generate (yellow circles) or require (green circles) NAD(P)H are indicated. Abbreviations for metabolites: Suc, sucrose; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; F1,6P, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phopshate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Ac-coA, acetyl-coA; Mal, malate; OA, oxaloacetate; Cit, citrate; Isocit, isocitrate; 2-OG, 2-oxoglutarate. Abbreviations for enzymes: G6PD, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; 6PGD, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; FBA, class-II fructose bisphosphate aldolase; FBP, fructose bisphosphatase; G3PD, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PK, pyruvate kinase; PEPS, PEP synthase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PFOR, pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; CS, citrate synthase; AcnB, aconitase, IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; GS, glutamine synthetase. Cyanophycin metabolism and the reported transfer to vegetative cells of the cyanophycin-derived dipeptide β-aspartyl-arginine [120] are not included in the scheme.