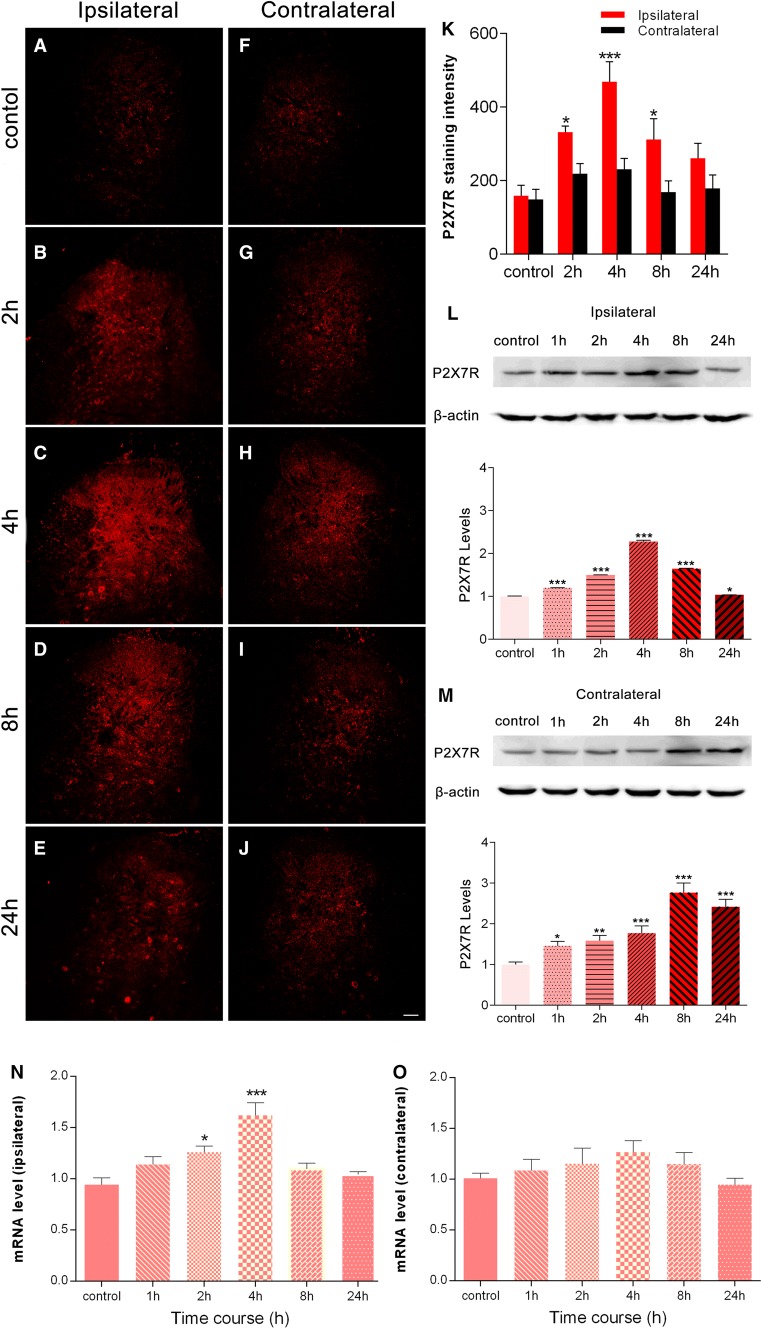
Fig. 1.
BmK I injection induces P2X7R activation in spinal dorsal horn. A–J Spatiotemporal distribution of P2X7Rs in the dorsal horn in the presence of BmK I. Compared with the control group (A, F), the BmK I-treated groups (B–E, G–J) showed marked P2X7R immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral dorsal horn. Increased ipsilateral P2X7R immunoreactivity indicated that P2X7R activation began at 2 h, peaked at 4 h, and gradually decreased by 24 h after BmK I administration. Scale bar, 100 μm (A–J). K Statistic results of P2X7R expression in bilateral spinal cord (n = 3; ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05 compared with control, two-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test; error bars indicate SEM). L, M Western blots and analysis of P2X7Rs in spinal cord after intraplantar injection of BmK I. Representative Western blots show the expression of P2X7Rs and β-actin in the ipsilateral (L) and contralateral (M) spinal cord; histograms show mean levels with respect to each control group at different time points after intraplantar BmK I injection. N, O mRNA expression in the ipsilateral (N) and contralateral (O) spinal cord. The data are presented as mean ± SEM of four rats per group (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with control, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test).