Figure 1.
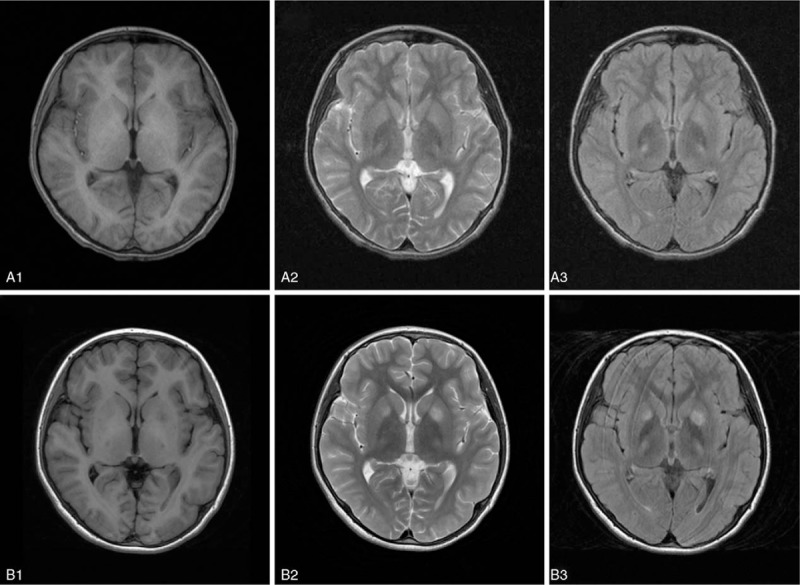
Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a patient with hepatic Wilson disease (WD) before and after a traumatic event. Normal signal on T1 (A1) and T2 (A2) weighted imaging, and high signals involving small areas of bilateral thalamus on flair (A3) weighted imaging 1 week before traumatic events. Low intensive signals involving small areas of left caudate nucleus and bilateral thalamus on T1-weighted imaging (B1), and high signals involving bilateral caudate nucleus and thalamus on T2 (B2) and flair (B3) weighted imaging 4.5 hours after traumatic event.
