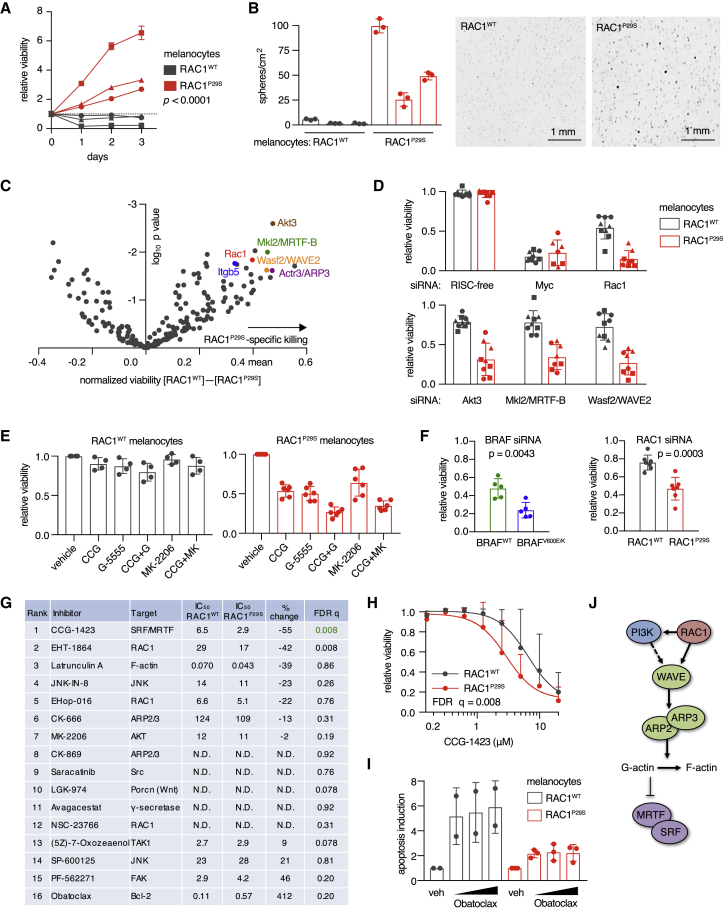
Figure 4.
Discovery of AKT and MRTF Dependencies in Cells with Endogenous RAC1P29S
(A) Melanocyte cultures from Rac1WT/WT and Rac1LSL−P29S/WT mice were grown in growth factor-reduced medium (FCS 0.25%, TPA-free) and assayed for viability using CellTiter-Glo; p value using two-way ANOVA for the genotype indicated.
(B) Single-cell suspensions of melanocytes from Rac1WT/WT and Rac1LSL−P29S/WT mice (n = 3 independent cultures per genotype) were seeded in soft agar for 3 weeks before imaging and automated counting.
(C) Melanocytes from Rac1WT/WT and Rac1LSL−P29S/WT mice were transfected with a custom siRNA library (n = 205 pools), grown in TPA-free medium for 3 days and assayed for viability (n = 3 independent cultures per genotype, each assayed in three independent experiments).
(D) Detailed plots of the data from the RAC1 effector siRNA screen presented in (C). Control siRNAs (top) and siRNAs that specifically kill melanocytes with endogenous RAC1P29S (bottom).
(E) Effect of combination treatments with inhibitors of the SRF/MRTF, PAK, and AKT pathways on viability of melanocytes with RAC1WT (left) or endogenous RAC1P29S (right). Mouse melanocyte cultures were grown in regular medium and assayed for viability 72 h after starting drug treatments. Inhibitor doses: CCG-203971 (SRF/MRTF) 10 μM, G-5555 (PAK) and MK-2206 (AKT) 2 μM.
(F) Effects on viability of human melanoma cell lines of reduction in expression of RAC1 or BRAF. Cells were cultured in growth medium and assayed for viability at 96 h post-transfection (n = 5 cell lines per genotype for the BRAF panel, n = 7 cell lines per genotype for the RAC1 panel, dots represent means of a single cell line that was tested in multiple independent experiments); p values from t test.
(G) Drug panel targeting RAC1 effectors applied in human melanoma cell lines with RAC1P29S versus cell lines with RAC1WT. Cells were cultured in growth medium and assayed for viability 72 h after starting drug treatments. Drugs ranked by the percentage difference between the half maximal inhibitory concentration (μM) of RAC1WT cell lines and RAC1P29S cell lines. For each drug, two-way ANOVA was used to probe the full dataset for a genotype effect, which was corrected according to Benjamini-Hochberg to produce FDR q values; N.D., not determined because curve fitting failed.
(H) Viability of human melanoma cell lines treated with the SRF/MRTF inhibitor CCG-1423 was determined using CellTiter-Glo (n = 7 cell lines per genotype, for each cell line the mean from two independent experiments was used); statistical analysis was performed as described in (F).
(I) Apoptosis of mouse melanocytes with endogenous RAC1P29S or RAC1WT cultured in growth medium and treated with obatoclax at 250 nM, 500 nM, or 1 μM for 3 days (n = 2–3 independent cultures per genotype).
(J) Schematic of the SRF/MRTF signaling pathway.
For all graphs: bars represent means ± SD. See also Figure S4.