Figure 5.
Effect of Ubiquitous Expression of RAC1P29SIn Vivo on Induction of B Cell Lymphoma
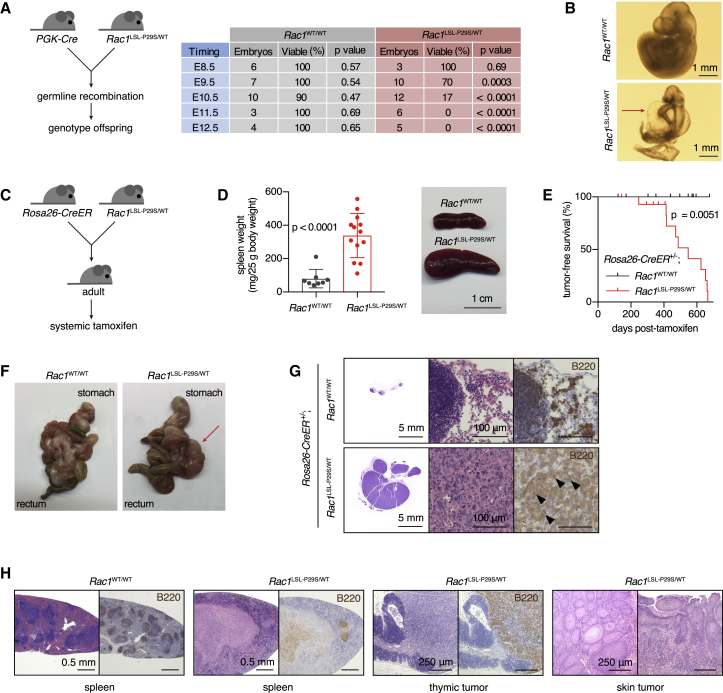
(A) Schematic of PGK-Cre/Rac1LSL−P29S cross and summary of results from the timed analysis of embryos. PGK-Cre was always maternal to ensure germline Cre recombination in all embryos. p values derived from chi-square testing are indicated.
(B) Representative micrographs showing gross cardiovascular abnormalities and developmental retardation in Rac1LSL−P29S/WT embryos (E10.5). Red arrow, enlarged pericardial cavity.
(C) Schematic of experimental design to express RAC1P29S in the whole body of adult mice. Tamoxifen was administered by oral gavage.
(D) Representative image of the spleen and quantification of spleen weight in aged mice with the indicated genotype. Bars represent means ± SD (n = 8–13 mice per genotype); Mann-Whitney test used for statistical comparison.
(E) Tumor-free survival curve of mice with indicated genotypes after treatment with tamoxifen. Result from log rank testing (Mantel-Cox) is indicated.
(F) Representative photos of the digestive tract from a Rosa26-CreER+/–;Rac1WT/WT mouse and a mesenteric lymphoma-bearing Rosa26-CreER+/–;Rac1LSL−P29S/WT mouse. Red arrow, lymphoma.
(G) Representative H&E- and B220-stained sections of a mesenteric lymphoma versus normal mesenteric lymph nodes in a control mouse.
(H) Representative H&E- and B220-stained sections of a normal spleen from a Rosa26-CreER+/–;Rac1WT/WT mouse and the spleen, thymic lymphoma, and squamous cell tumor of the skin from Rosa26-CreER+/–;Rac1LSL−P29S/WT mice.
See also Figure S5.