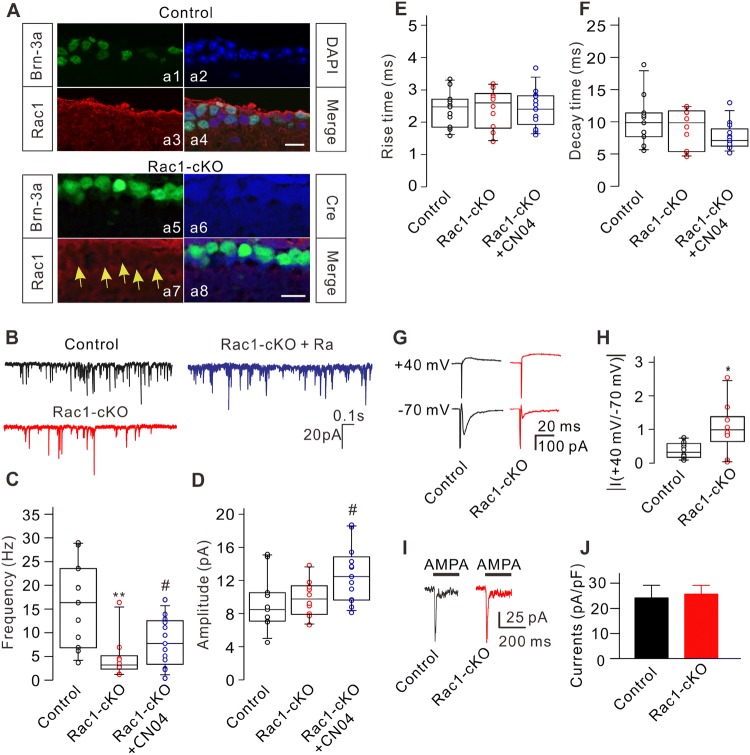
Fig. 1.
Conditional knockout of Rac1 modulates excitatory synaptic transmission of RGCs. A Triple immunofluorescence labeling showing the expression of Brn-3a (a1), DAPI (a2), and Rac1 (a3) in a retinal slice from a control mouse at P17 (a4: merged image of a1, a2, and a3). Triple immunofluorescence labeling showing the expression of Brn-3a (a5), Cre recombinase (a6), and Rac1 (a7) in a retinal slice from an Rac1-cKO mouse at P17 (a8: merged image of a5, a6, and a7). Arrows indicate RGCs lacking Rac1 expression. Scale bars, 10 μm. B Representative recordings of mEPSCs in RGCs from control, Rac1-cKO, and Rac1-cKO+CN04 retinal slices. C–F Summary data showing that conditional deletion of Rac1 in RGCs reduced the frequency (C), but not the amplitude (D) and kinetics (E, F) of mEPSCs. CN04 administration partially rescued the decreased frequency of mEPSCs in RGCs from Rac1-cKO mice (n = 11-13; **P < 0.01 vs control, #P < 0.05 vs Rac1-cKO). G Representative recordings showing the changes in amplitude of eEPSCs from RGCs in retinal slices at holding potentials of +40 mV and –70 mV in control and Rac1-cKO mice. H Summary data showing the average ratios of the current amplitudes at +40 mV and –70 mV in RGCs from control (n = 9) and Rac1-cKO (n = 8) mice (*P < 0.05 vs control). I Representative recordings from two RGCs acutely isolated from control and Rac1-cKO mice, showing no significant difference in the currents induced by AMPA (100 μmol/L). J Summary data showing the average AMPA current densities in RGCs acutely isolated from control (n = 10) and Rac1-cKO (n = 9) mice. The distribution of data in each cell was indicated as scattered circles and the data are expressed as medians and interquartile ranges.