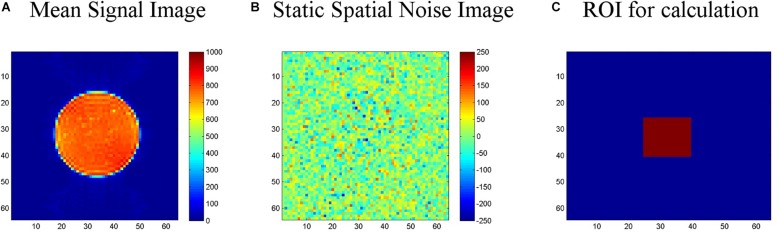
FIGURE 2.
Calculation of the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) for the gel phantom. (A) First, a “signal image” is calculated as the voxel-wise average of the center slice of the gel phantom (slice-of-interest, SOI) across the time series. (B) Second, a “static spatial noise image” is calculated as the voxel-wise difference of the sum of all odd images and the sum of all even images in the SOI. (C) Third, the SNR is defined as the quotient of the average intensity of the mean signal image in a region of interest (ROI, 15 × 15 voxel), located in the center of the phantom of the SOI, and the standard deviation of the static spatial noise within the same ROI.