Figure 1.
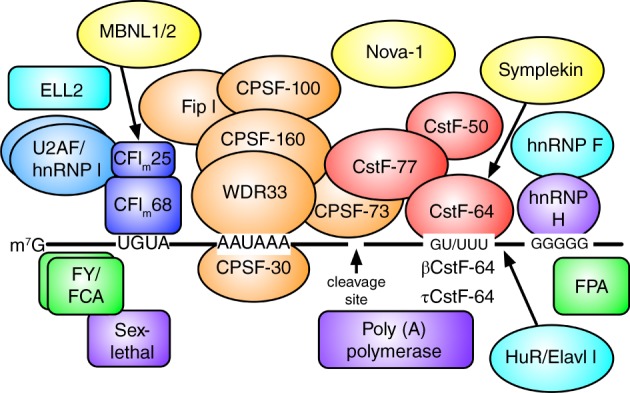
Core and auxiliary proteins involved in tissue‐specific alternative polyadenylation. The pre‐mRNA (black line) consists of upstream sequence elements (UGUA), the polyadenylation signal (AAUAAA), a cleavage site (arrow), the downstream sequence element (GU/UUU), and the downstream G‐rich element (GGGGG). The core polyadenylation proteins consist of the CPSF proteins, the CstF proteins, and CFIm (see the text for details), and the template‐independent poly(A) polymerase is indicated. Auxiliary (U2AF, hnRNP F, hnRNP H, hnRNP I) and tissue‐specific (Nova‐1, βCstF‐64, τCstF‐64, ELL2, MBNL1/2, HuR/Elavl1, sex‐lethal, FPA, FY, and FCA) proteins are indicated. It is not entirely clear whether symplekin is a core or an auxiliary polyadenylation protein, but it interacts directly with CstF‐64
