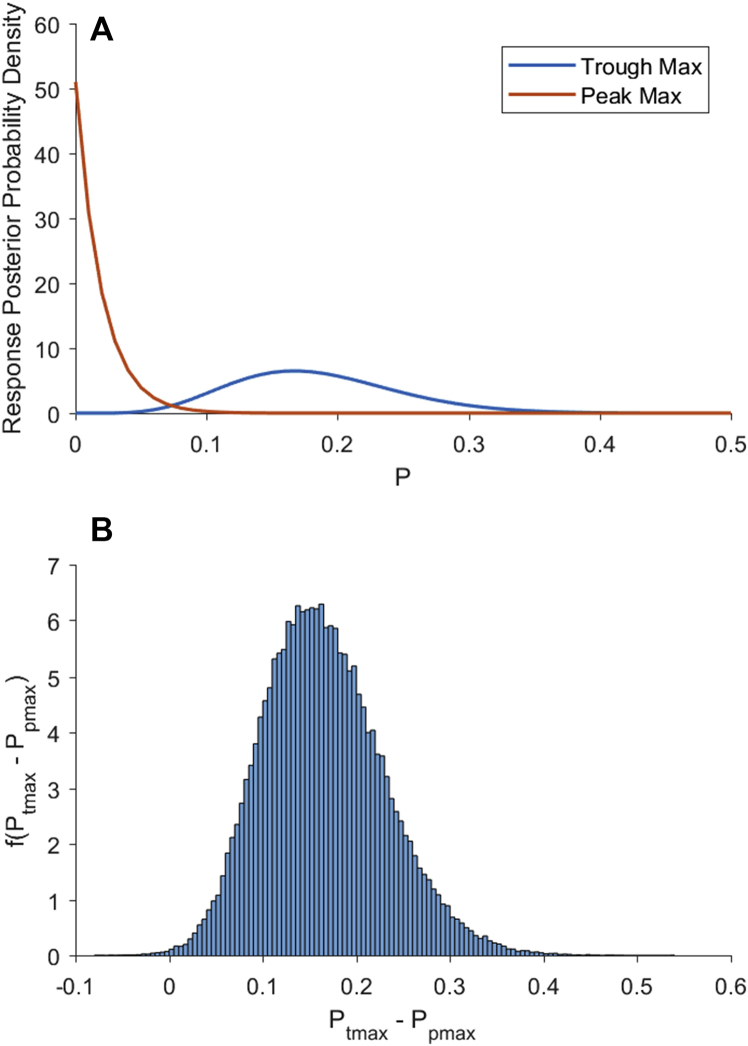
Figure 1.
Bayesian analysis of the probability of responding as a function of EEG signatures using a beta-binomial model.3 (A) Blue curve is f(ptmax), the posterior probability density of responding during the isolated forearm test given a trough-max EEG pattern. Orange curve is f(ptmax), the posterior probability density of responding during the isolated forearm test given a peak-max/burst suppression EEG pattern. (B) Probability density of the difference between the trough-max and the peak-max probability of responding computed by Monte Carlo convolution.3 The probability density f(ptmax − ppmax), gives the probability that the trough-max probability of response is greater than the peak-max probability of response. The probability that the trough max response probability is greater than the peak-max probability is 0.9984 (area under the curve to the right of zero). Hence, the trough-max and peak-max groups can be distinguished with near certainty.