Figure 8.
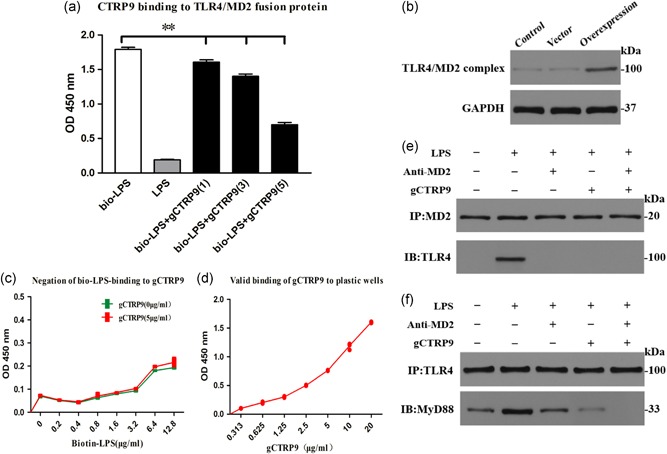
gCTRP9 inhibits TLR4/MD2 complex formation. (a) The competitive binding of bio‐LPS and gCTRP9 to the designed LPS trap was studied by using an ELISA‐based assay. The bio‐LPS (1 μg/ml) and LPS (100‐fold dose) emulously combined with the LPS trap (lanes 1 and 2). The ability of three doses (μg/ml) of CTRP9 to competitively bind bio‐LPS to the LPS trap was tested (lanes 3–5). (b) The construction of TLR4 and MD2 fusion proteins was confirmed by western blot analysis. (c) ELISA‐based analysis of the ability of bio‐LPS to bind to gCTRP9. (d) Verification of the ability of gCTRP9 to effectively bind to the plastic plate in the ELISA system. (e, f) Representative western blot (IB) from a coprecipitation (IP) experiment showing the effects of CTRP9 and anti‐MD2 on MD2/TLR4 complex formation (e) and TLR4/MyD88 complex formation (f). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments, **p < 0.01; the connection represents a comparison between the two groups. CTRP9: C1q/TNF‐related protein‐9; ELISA: enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MyD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88; SEM: standard error of the mean; TLR4: toll‐like receptor 4 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
