Figure 1.
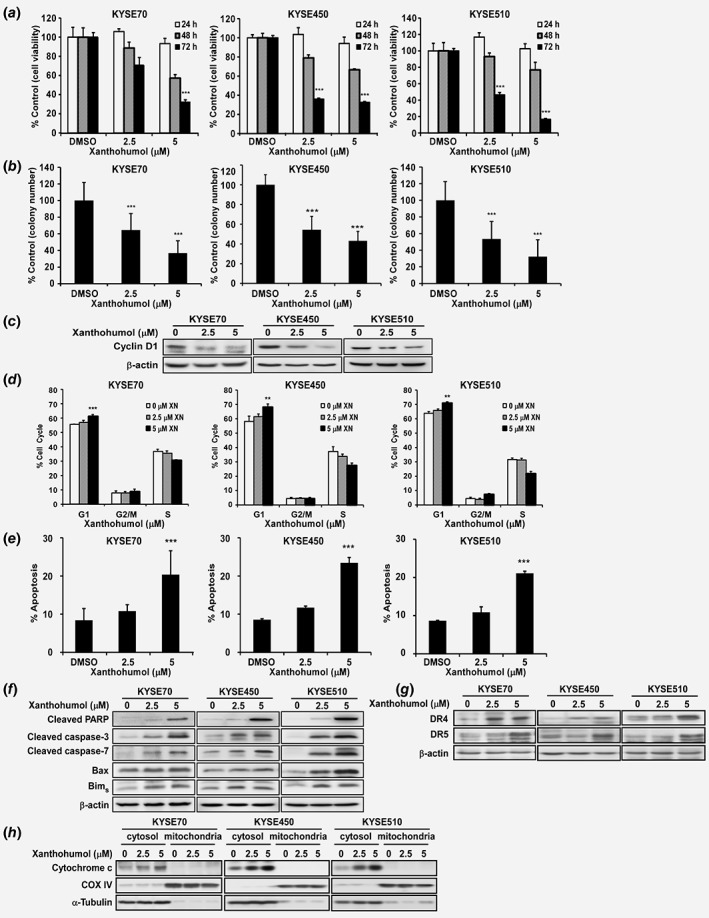
Xanthohumol inhibits esophageal cancer cell growth. (a) Cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay. Data show that xanthohumol inhibits ESCC cell growth in a dose‐dependent manner. (b) Xanthohumol decreases colony formation in soft agar. Asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) indicate a significant reduction in cancer cell growth and colony formation. (c) Xanthohumol reduces cyclin D1 as determined by Western blot analysis (48 hr post treatment). (d) Xanthohumol treatment leads to cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase at 48 hr. (e) Xanthohumol treatment increases apoptosis at 72 hr based on annexinV+/PI− gating. (f–h) Apoptotic protein markers are increased after xanthohumol treatment (Western blot detection at 72 hr post treatment). Asterisks (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) indicate a significant change in cell cycle and apoptosis.
