Figure 5.
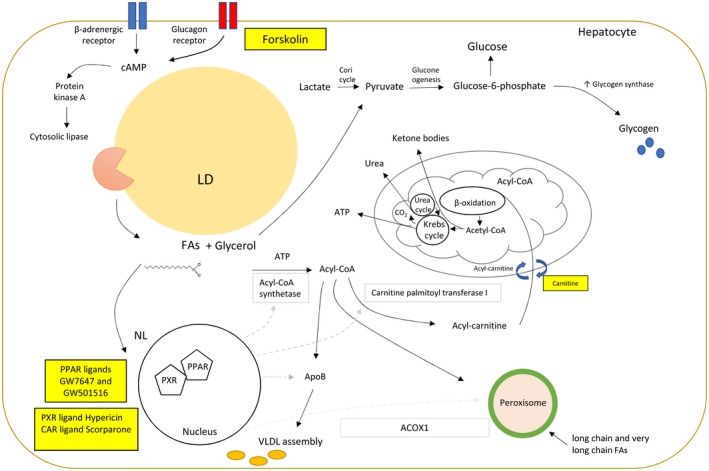
A suggested relationship between the defatting cocktail and intracellular lipolytic metabolic pathways. Forskolin activates the glucagon membrane receptors, which in turn stimulate the cAMP–protein kinase A pathway; thus, the cytoplasmic lipases are attracted to the surface of LDs. Glycerol and FFAs will then be released, serving not only as substrates for the cell metabolism but also as ligands to nuclear receptors (PPAR and liver X receptor), increasing the transcription of enzymes involved in the catabolism of FFAs in the mitochondria and peroxisome. Diverse cocktail drugs (GW7647, GW501516, hypericin, scorparone) also act as ligands to other nuclear receptors (PXRs and CARs), boosting the transcription of key enzymes. Cytosolic FA reacts with ATP, producing fatty acyl‐CoA. Acyl‐CoA in turn reacts with apolipoprotein B to generate lipoproteins to be exported from the cell and/or reacts with the hydroxyl group of carnitine via carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Acyl‐carnitine is transported inside the mitochondria by a carnitine‐acyl‐CoA transferase, and a carnitine is transferred outside. Acyl‐CoA is processed by β‐oxidation. The acetyl‐CoA produced then will follow to ketogenesis or for complete oxidation via the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain with the production of ATP. Increased production of aspartate and CO2 stimulate the urea cycle, increasing the production of urea. Alternatively, long chain and very long chain FFAs are also oxidized in the peroxisomes. Glycerol is a gluconeogenic precursor; it is converted to pyruvate, producing glucose‐6‐phosphate through the gluconeogenesis pathway. Glucose‐6‐phosphate will be released as glucose in the perfusate and stimulate the enzyme glycogen synthase, increasing the production of glycogen. The squares contain the specific enzymes that have an up‐regulation in the transcription as a consequence of this stimulus. Drugs and supplement used in the cocktail are presented in yellow squares.
