Figure 4.
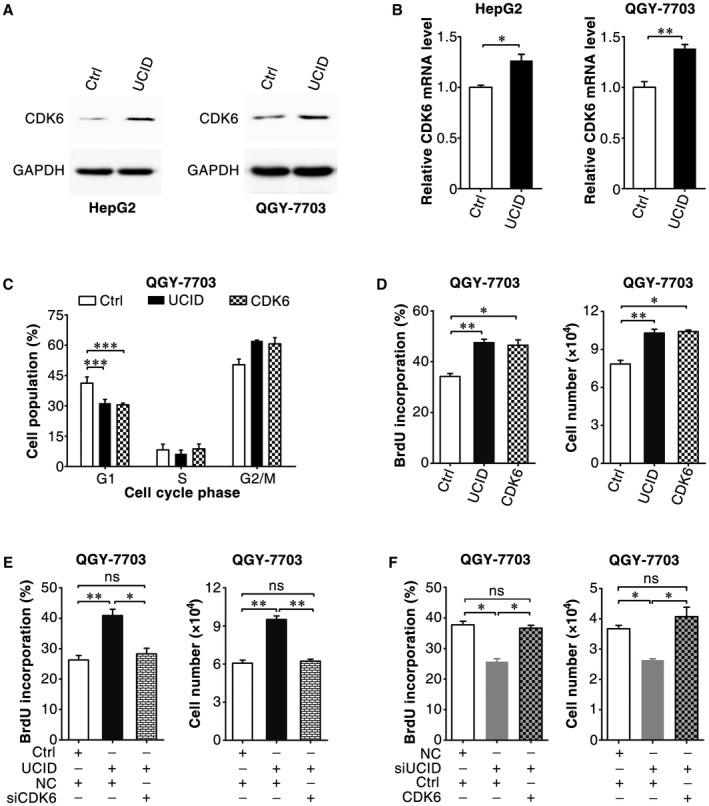
Lnc‐UCID overexpression promotes G1/S transition by enhancing CDK6 expression. (A,B) Ectopic lnc‐UCID expression increased the protein and mRNA levels of CDK6. HepG2 or QGY‐7703 cells were transfected with the pc3‐puro (Ctrl) or pc3‐puro‐UCID plasmid for 24 hours, followed by culture with puromycin for 48 hours; then, the cells were subjected to western blotting (A) or quantitative real‐time PCR (B) analysis. (C) Ectopic lnc‐UCID and CDK6 expression promoted G1/S transition. pc3‐gab (Ctrl), pc3‐gab‐UCID, and pc3‐gab‐CDK6‐transfected cells were synchronized with nocodazole before FACS analysis. (D) Ectopic lnc‐UCID and CDK6 expression increased DNA replication and promoted cell growth. (E) Silencing CDK6 abrogated the lnc‐UCID‐promoted DNA replication and cell growth. (F) CDK6 expression rescued the siUCID‐induced reductions in DNA replication and cell growth. For (D)‐(F), QGY‐7703 cells were transfected twice at 24‐hour intervals with the indicated plasmids. Twenty‐four hours after the last transfection, the cells were reseeded, transfected with the indicated siRNA duplex (E,F), and then subjected to BrdU incorporation or cell counting assays (D‐F). For cell counting assay, 1 × 104 transfected QGY‐7703 cells were seeded on day 0 and counted on day 4. For (B)‐(F), error bars represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
